-
What Is Hadoop Cloud Storage?
-
Why Use Cloud Storage With Hadoop?
-
Method 1. Setting Up Hadoop With AWS S3
-
Method 2. Integrating Hadoop With Azure Blob Storage
-
Method 3. Integrating Hadoop With Google Cloud Storage
-
Protecting Your Data in Hadoop Cloud Storage With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Hadoop Cloud Storage FAQs
-
Conclusion
Hadoop has long been the backbone of big data storage and processing. But as data volumes grow and business needs change, more organizations are moving Hadoop workloads to the cloud. Why? Cloud storage offers flexibility, scalability, and cost savings that on-premises Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) can’t match. In this article, we’ll explore what Hadoop cloud storage is, why it matters, and how to integrate Hadoop with leading cloud storage solutions like AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Storage. We’ll also show you how to protect your Hadoop cloud data with Vinchin.
What Is Hadoop Cloud Storage?
Hadoop cloud storage means using cloud-based object storage services as either primary or secondary storage layers for your Hadoop clusters. Instead of relying only on HDFS running on local disks or servers in your data center, you let Hadoop read from—and write directly to—cloud services such as Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, or Google Cloud Storage.
This approach decouples compute from storage. That means you can scale up processing power when needed without worrying about running out of disk space—or paying for unused hardware when demand drops.
Key Differences Between HDFS and Cloud Object Storage
While both HDFS and cloud object stores hold large datasets reliably, they work differently behind the scenes:
HDFS is a distributed file system designed for high-throughput access to large files across many nodes.
Cloud object stores like S3 or GCS store data as objects in buckets rather than files in directories; some file system operations behave differently or may be slower.
Object stores offer built-in redundancy across regions but may have higher latency compared to local disks.
Understanding these differences helps you plan migrations or hybrid architectures without surprises.
Why Use Cloud Storage With Hadoop?
Moving Hadoop storage to the cloud brings several benefits worth considering before making any changes.
First off, cloud storage is elastic—you can scale up or down as your data grows without buying new hardware or overprovisioning resources upfront. Second, you pay only for what you use instead of maintaining expensive on-premises clusters that might sit idle much of the time.
Thirdly, cloud providers build durability into their platforms, often replicating your data across multiple locations automatically so you don’t need extra backup scripts just to avoid losing information during outages.
Finally—and perhaps most importantly—decoupling compute from storage lets you spin up powerful clusters only when needed: process petabytes today; shut them down tomorrow while leaving all raw data safely stored in the cloud until next time.
Method 1. Setting Up Hadoop With AWS S3
Amazon S3 remains one of the most popular choices for storing big datasets outside traditional infrastructure boundaries. Integrating it with Hadoop unlocks massive scalability—but requires careful setup.
Before starting configuration changes on production systems:
Always test changes in a non-production environment first
Back up existing configuration files
Review AWS IAM policies regularly
Configuring core-site.xml Securely
To connect Hadoop with S3:
1. Open your core-site.xml file
2. Add properties such as fs.s3a.access.key, fs.s3a.secret.key, fs.s3a.endpoint, and fs.s3a.impl
For example:
<property> <name>fs.s3a.access.key</name> <value>YOUR_AWS_ACCESS_KEY</value> </property> <property> <name>fs.s3a.secret.key</name> <value>YOUR_AWS_SECRET_KEY</value> </property> <property> <name>fs.s3a.endpoint</name> <value>s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com</value> </property> <property> <name>fs.s3a.impl</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.fs.s3a.S3AFileSystem</value> </property>
For better security in production environments:
Use IAM roles attached directly to EC2 instances instead of hardcoding credentials
Limit permissions strictly using AWS Identity & Access Management (IAM)
Method 2. Integrating Hadoop With Azure Blob Storage
Azure Blob Storage provides scalable object-based repositories ideal for big-data workloads—including those powered by Apache Hadoop clusters hosted anywhere.
You can connect via two main connectors:
1. The legacy wasb
2. The newer recommended abfs (for Azure Data Lake Gen2)
Setting Up core-site.xml For abfs Connector
For modern deployments (Hadoop v2.x+), use abfs:
<property> <name>fs.azure.account.key.youraccount.dfs.core.windows.net</name> <value>YOUR_ACCOUNT_KEY</value> </property>
Replace youraccount with your actual account name; set key value accordingly (find it under Access Keys in Azure Portal).
For older setups still using wasb:
<property> <name>fs.azure.account.key.YOUR_ACCOUNT_NAME.blob.core.windows.net</name> <value>YOUR_ACCOUNT_KEY</value> </property>
For improved security:
Prefer Managed Identities over static keys wherever possible
Method 3. Integrating Hadoop With Google Cloud Storage
Google Cloud Storage (GCS) offers strong consistency guarantees plus seamless integration with other Google analytics tools—a great fit if already invested in GCP ecosystem components like BigQuery or Dataproc clusters!
The official connector (gcs) comes pre-installed on most recent distributions but always verify compatibility before deploying at scale.
Configuring Service Account Credentials Safely
You need a service account key JSON file granting proper permissions (Storage Object Admin role recommended):
<property> <name>google.cloud.auth.service.account.json.keyfile</name> <value>/path/to/keyfile.json</value> </property> <property><name>fs.gs.project.id</name><value>your-gcp-project-id</value></property>
Alternatively set environment variable GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS=/path/to/keyfile.json.
Never embed sensitive credentials inside shared scripts! Restrict access tightly using GCP IAM controls.
Protecting Your Data in Hadoop Cloud Storage With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
With critical business data now residing in various cloud environments through platforms like Amazon S3, ensuring robust protection becomes essential for operational continuity and compliance requirements alike. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as an enterprise-level database backup solution supporting today's mainstream databases—including Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—with broad compatibility across public/private clouds and virtualized infrastructures.
Among its extensive feature set are incremental backup capabilities (for Oracle/MySQL/MariaDB), advanced source-side compression (for Oracle/SQL Server/MariaDB), batch database backup management across multiple platforms at once, granular retention policies including GFS retention strategies tailored for regulatory needs, plus comprehensive integrity checks and recovery verification via SQL scripts—all designed to maximize efficiency while minimizing risk exposure throughout complex hybrid-cloud deployments.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery makes safeguarding databases simple through its intuitive web console interface:
Step 1. Select the Hadoop HDFS files you wish to back up
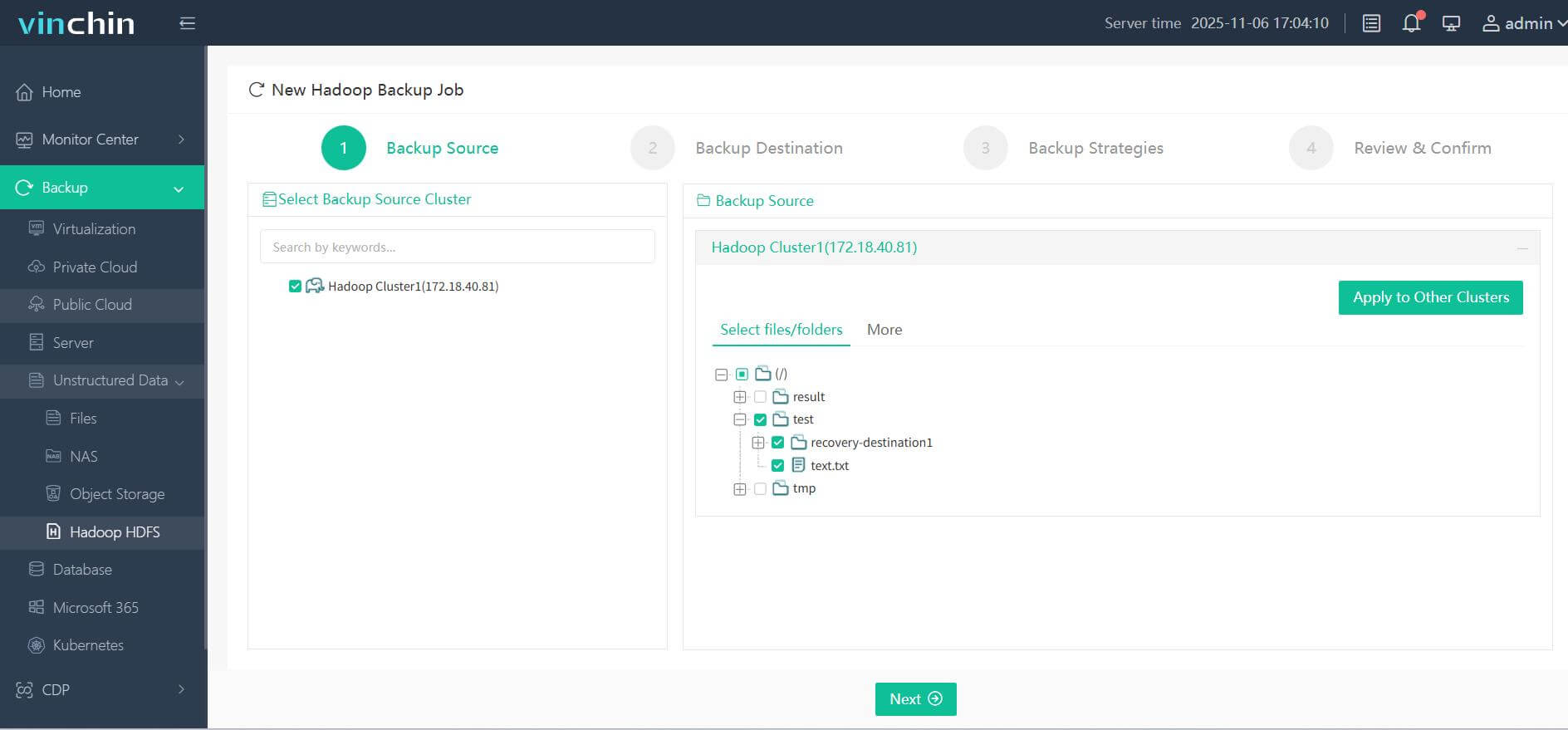
Step 2. Choose your desired backup destination
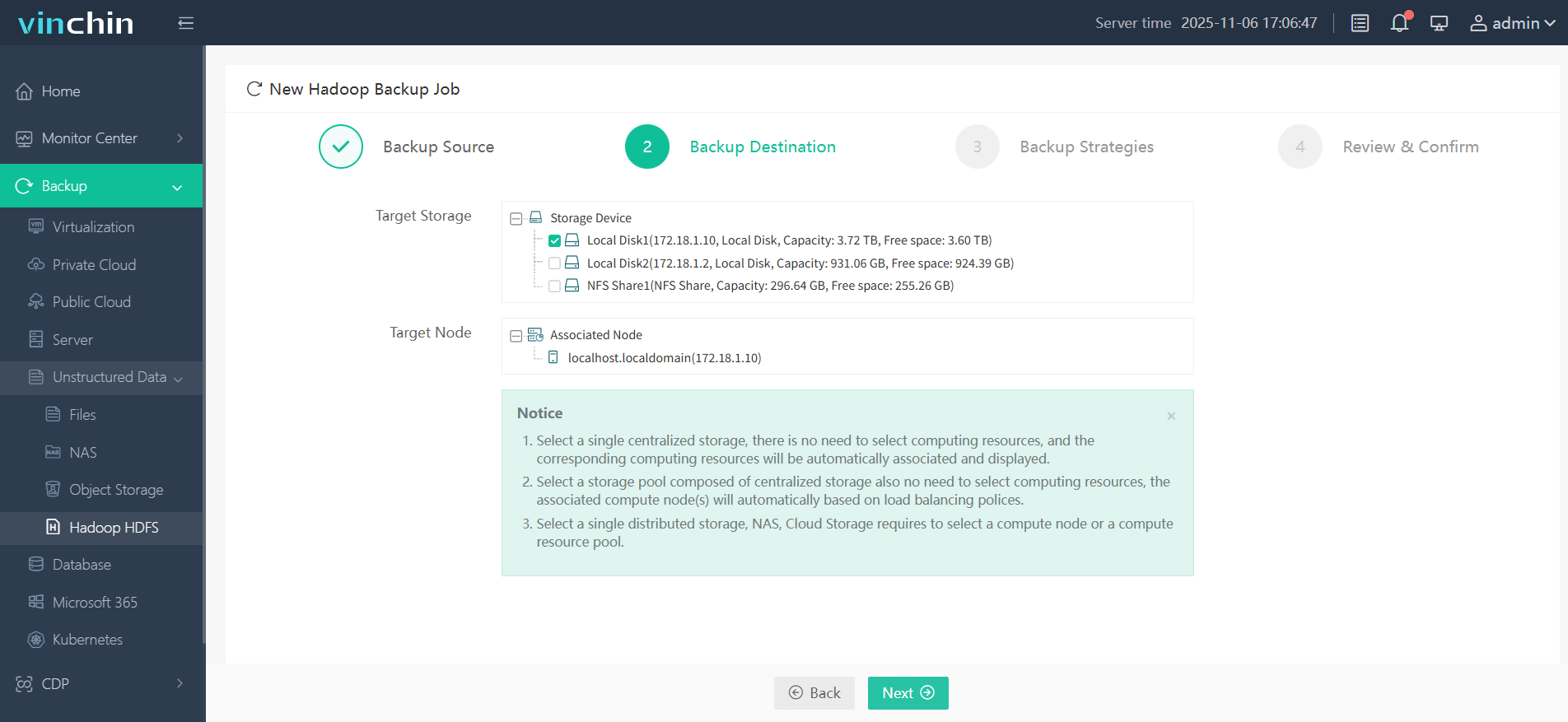
Step 3. Define backup strategies tailored for your needs
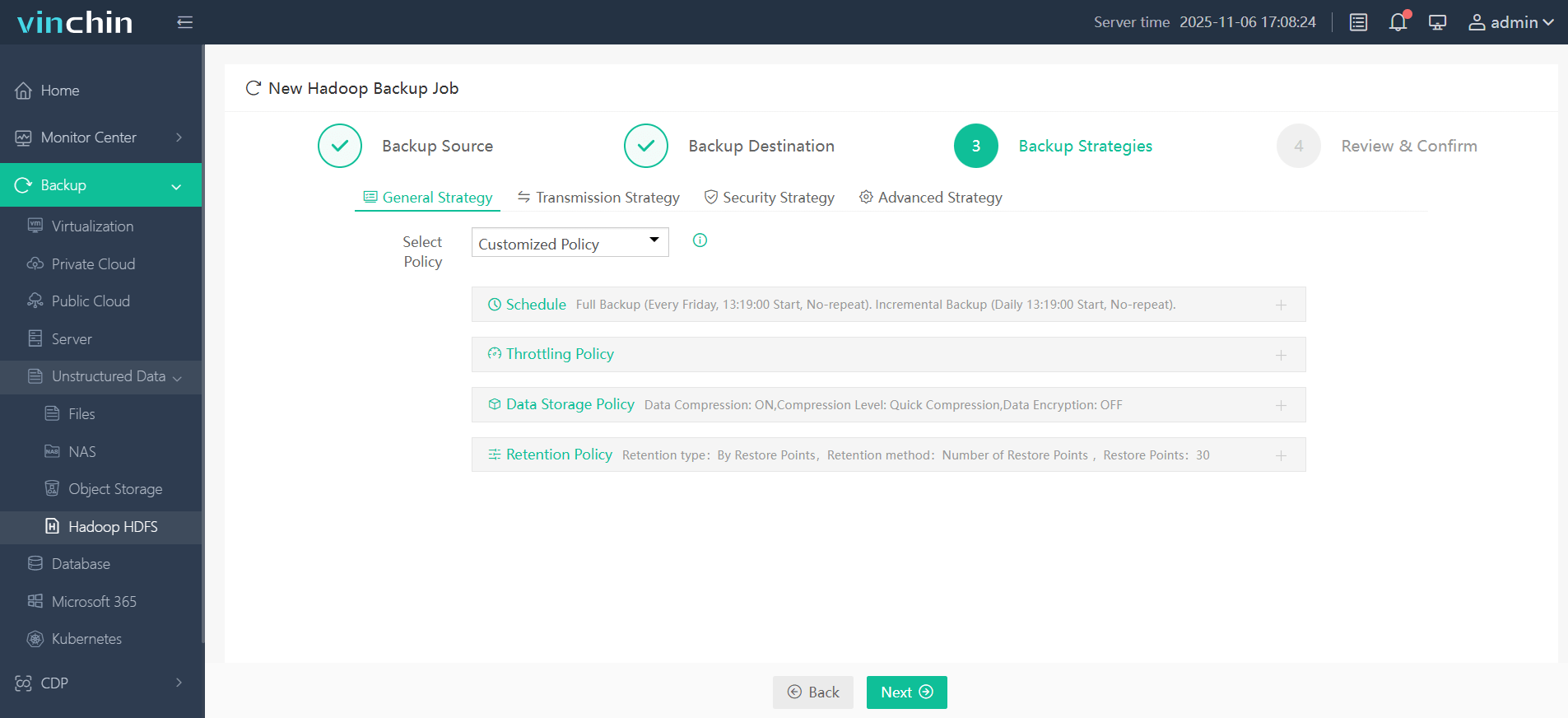
Step 4. Submit the job
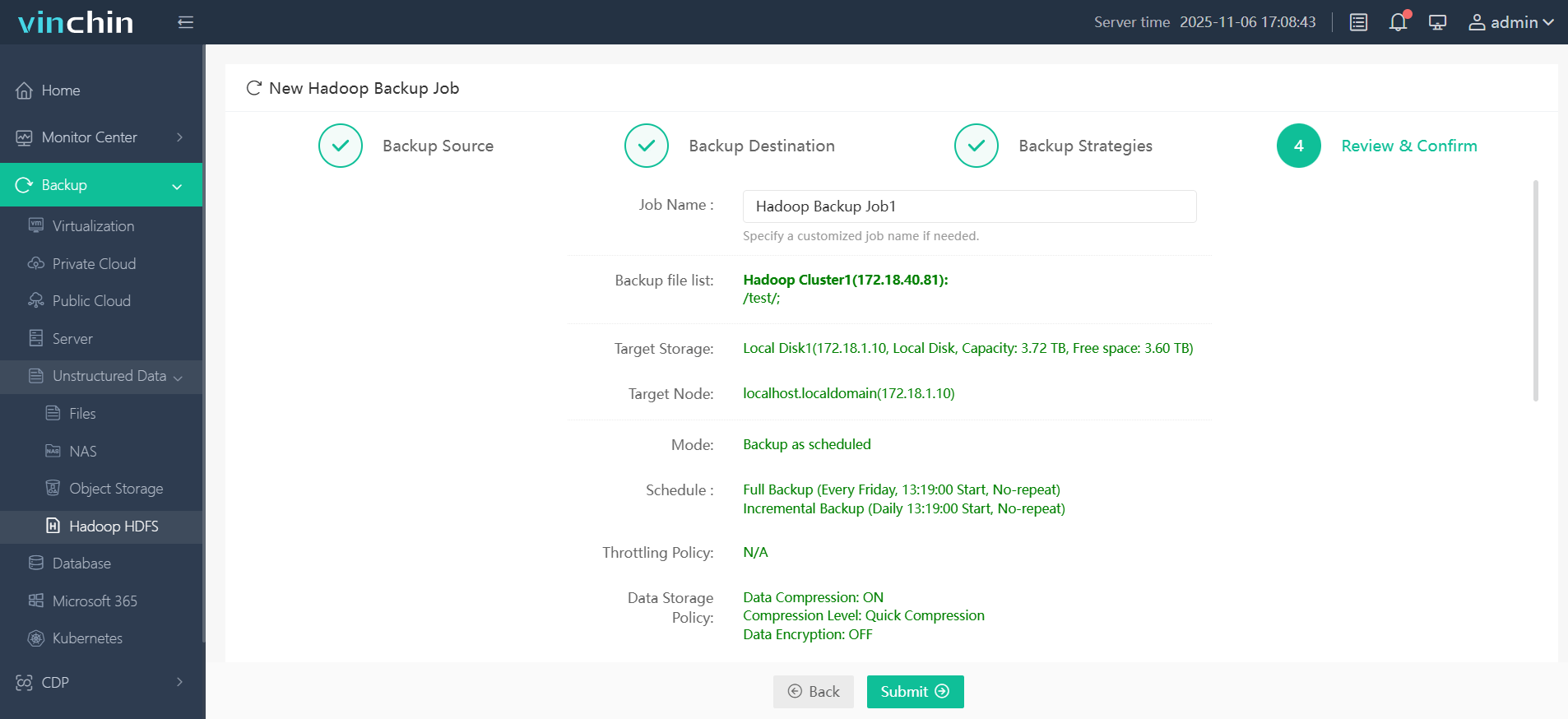
Recognized globally by enterprises large and small—with top ratings from industry analysts—you can experience every feature free for 60 days by clicking download below!
Hadoop Cloud Storage FAQs
Q1: Can I migrate existing HDFS data to cloud storage without downtime?
A1: Yes—you can use DistCp tool (hadoop distcp hdfs:///source s3a:///target) while keeping both source/destination online throughout transfer window!
Q2: Does using cloud storage with hadoop affect job performance?
A2: Some operations may experience higher latency versus local disks—but tuning parallelism/cache sizes plus batching writes helps offset impact significantly over time!
Q3: How do I secure access control lists around buckets used by hadoop jobs?
A3: Always assign least privilege roles via IAM/service accounts—not static passwords—and audit permissions regularly across all environments involved!
Conclusion
Hadoop cloud storage unlocks new levels of scalability,fault tolerance,and cost savings across modern big-data platforms.By integrating seamlessly with AWS/Azure/GCP,you gain freedom from hardware constraints plus global reach.Vinchin makes protecting this critical information easy—try our free trial today!
Share on:






