-
Local storage (On‑premises storage)
-
Cloud backup
-
Hybrid backup
-
Best practices for data backup
-
Introducing Vinchin for unified VM protection
-
Safest place to backup data FAQs
-
Conclusion
In a data-first world, backups aren't optional—they're essential. If you manage critical virtual machines or sensitive business data, your backup solution must be secure, reliable, and scalable. So where is the safest place to store that backup data?
We'll explore local storage, cloud backup, and hybrid approaches, then lay out best practices and introduce a professional tool to make it all work.
Local storage (On‑premises storage)
Local storage means keeping backup data in your own data center—using DAS, NAS, SAN, or tape libraries.
It offers fast recovery and total control, ideal for large VM environments like Proxmox, VMware, or Hyper‑V. Since data stays on the internal network, you can often meet a sub-hour RTO.
To enhance safety, isolate backup systems physically from production networks. Use RAID‑6 for redundancy or RAID‑10 for performance, and enable immutable storage (WORM or object-lock NAS) to block tampering.
Air‑Gap protection is also key. Use standalone NAS devices that stay powered off during production hours or handle tape backups manually to keep them completely offline.
Cloud backup
Cloud backup stores data in third-party data centers like AWS, Azure, or cloud-specific platforms. It brings scalability and regional redundancy—great for distributed setups like OpenStack or XenServer.
Pay attention to the shared responsibility model. You must manage encryption and keys yourself. Choose services with AES‑256 encryption, TLS 1.2+ transfer, and compliance zones like FIPS 140‑2 or GDPR.
Also, watch for egress fees when retrieving data. Use cold storage (like AWS Glacier) to save costs on rarely used data—but expect longer recovery times.
Hybrid backup
Hybrid backup merges the speed of local recovery with the resilience of the cloud. It's the most versatile approach, especially for platforms like Proxmox, VMware, RHV, or oVirt.
Keep mission‑critical VM backups locally for fast RTO. At the same time, sync secondary or archive data to cloud cold storage at intervals—whether scheduled, real‑time, or eventually consistent.
Tools like Rclone help optimize data tiering. Combine local deduplication and compression to reduce bandwidth use.
This model also supports compliance, e.g., financial or healthcare data that must reside in specific regions. Pair it with a disaster recovery (DR) runbook to define which systems restore locally and which from the cloud.
Best practices for data backup
Backup isn't just storage—it's strategy. These principles ensure your data stays protected, recoverable, and compliant.
✅ 3‑2‑1‑1‑0 Rule
3 copies of data (including production)
2 different media types (e.g., disk + tape)
1 off-site copy
1 immutable or offline copy
0 validation errors
This approach prevents both hardware failure and ransomware threats. Immutable and air-gap layers give you real protection.
✅ Encryption Standards
Use AES‑256 for data at rest
Use TLS 1.2+ for data in transit
For regulated environments, select FIPS 140‑2–compliant solutions
You must control your encryption keys—not the provider.
✅ Restore Validation
It's only a backup if it restores. Automate at least one full restore test per month. Power up a VM and verify it boots. Integrate this into CI/CD pipelines for DevOps teams.
✅ Logging and Monitoring
Log every backup task—success, failure, or skip. Protect your backup console with RBAC and MFA. Stream logs into systems like ELK or Graylog for real-time inspection.
✅ Compliance Assurance
Ensure your backup solution supports GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2 by logging retention, access, and destruction events. Use WORM or object lock to keep those logs tamper-proof.
✅ Recovery Benchmarks
| Storage Type | RTO | RPO | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local SSD (RAID 10) | < 15 minutes | < 1 hour | Fast recovery; no off-site copy |
| Offline tape | > 24 hours | ≈24 hours | Low cost, long retention, slow |
| Cloud hot storage | 1–2 hours | 1–4 hours | Scalable; watch egress fees |
| Cloud cold storage | > 12 hours | ≈1 day | Very low cost; recovery delayed |
Introducing Vinchin for unified VM protection
No matter where your backup data lives—on-prem, cloud, or hybrid—you need a tool that unifies them all.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional, enterprise-grade VM backup solution compatible with over 15 major virtualization and cloud platforms. It supports volume backup, tape backup, and cloud backup, providing a comprehensive solution for various backup needs.
Vinchin offers full backup, incremental, differential, and scheduled/repetitive backup methods. It includes data deduplication and compression, V2V cross-platform migration, and GFS retention policies to reduce storage use and simplify long-term management. It also supports LAN-Free backup, SpeedKit acceleration, quiesced snapshots (VMware), HotAdd (VMware), and CBT across platforms—ensuring backup speed and consistency.
Using Vinchin is easy. For example, backing up a Proxmox VM takes just four steps:
1. Select the Proxmox VM to back up;
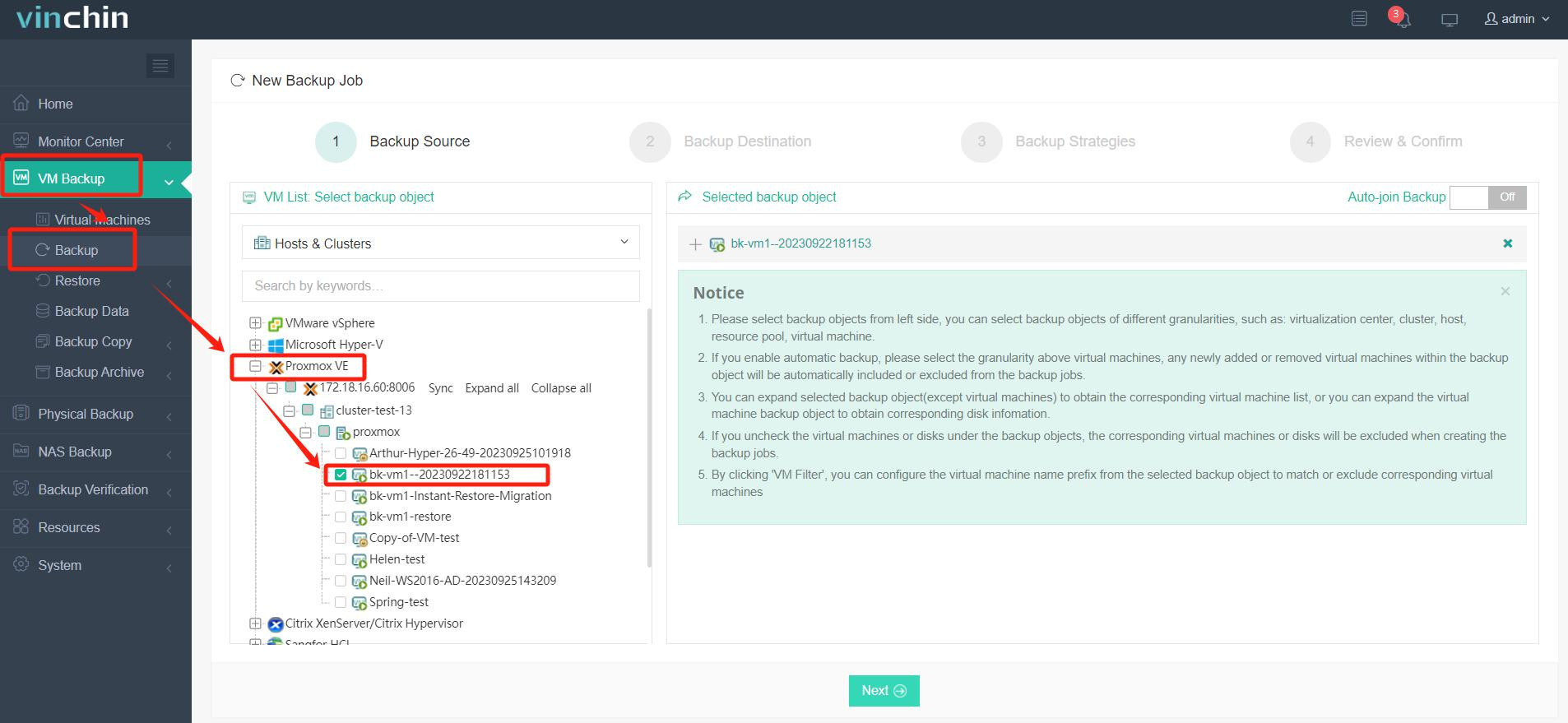
2. Choose backup storage;
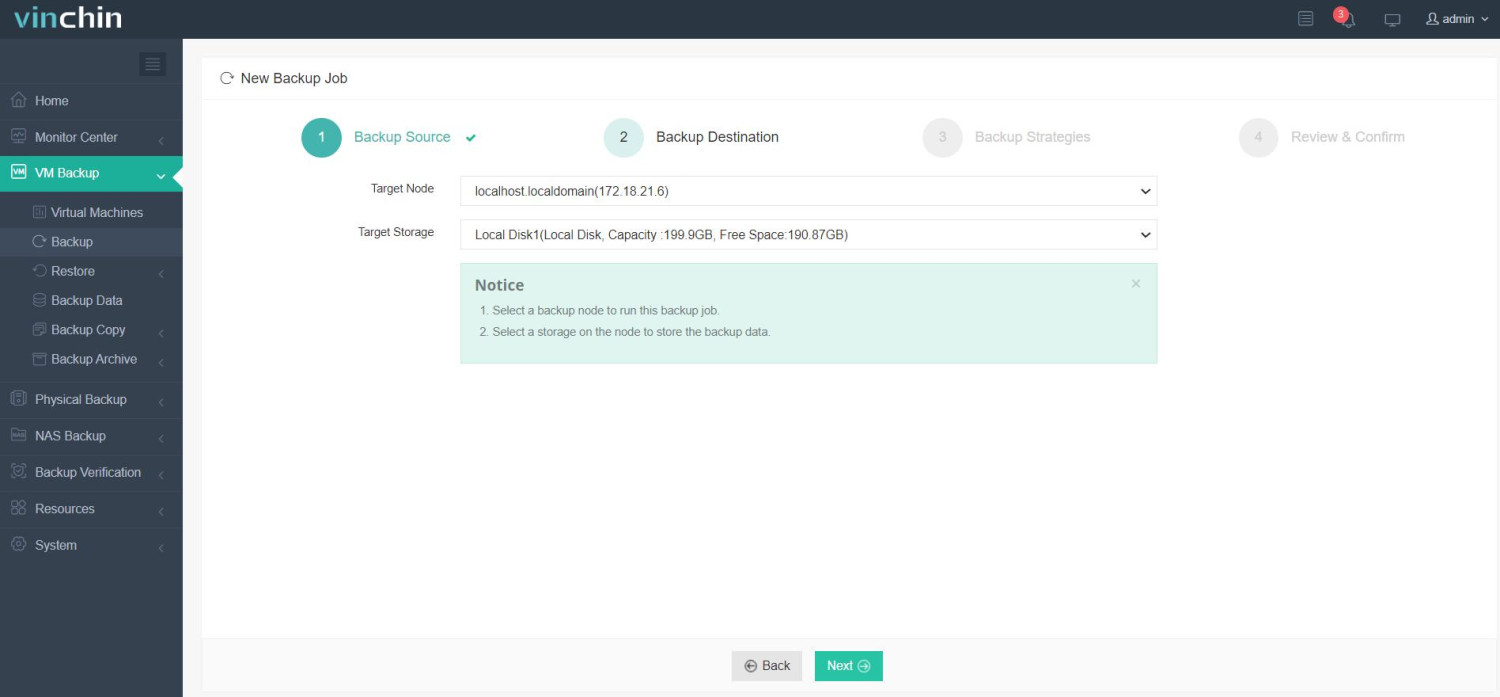
3. Configure backup strategies;
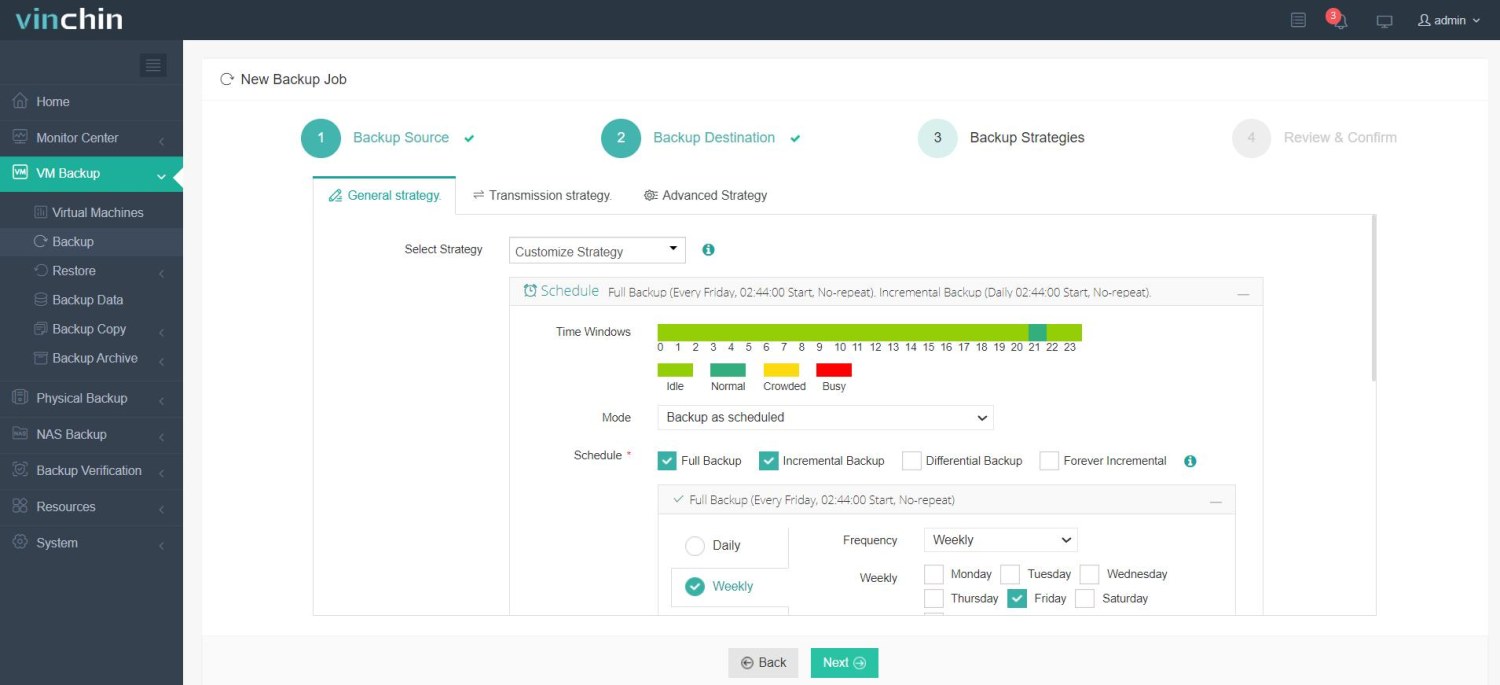
4. Submit the job.
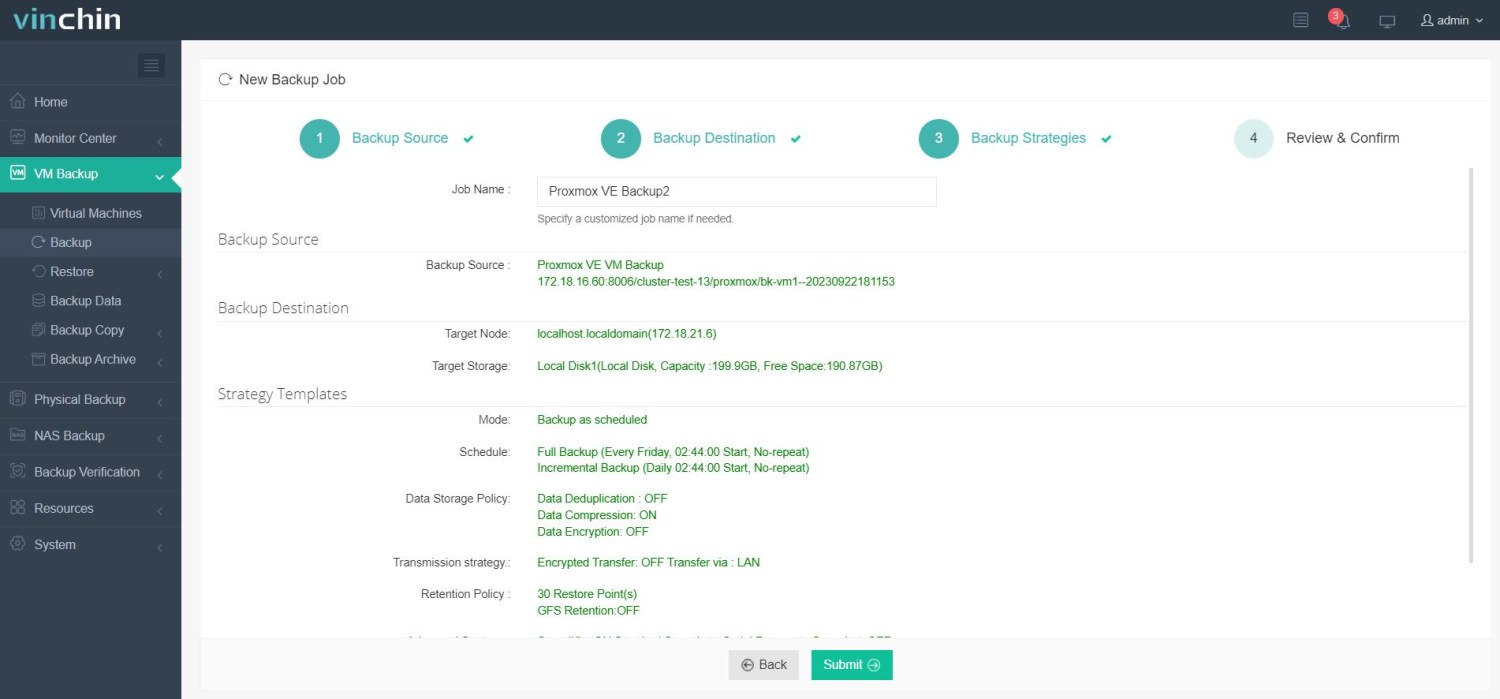
Vinchin protects thousands of businesses worldwide and earns strong reviews. Start your 60-day full-featured free trial today and deploy in minutes.
Safest place to backup data FAQs
Q1: How do I create an offline, immutable backup?
Store it in S3 with object lock enabled or use write-protected tape.
Q2: How can I reduce cloud backup costs?
Enable deduplication and compression locally, and tier cold data with lifecycle rules.
Q3: How often should I test restores?
At least monthly; for DevOps, automate it in your CI/CD pipeline.
Conclusion
There is no single safest place for backups—only smart strategies. Local storage ensures fast recovery, cloud adds redundancy and scale, and hybrid blends both. Using the 3-2-1-1-0 rule, strong encryption, compliance, and tools like Vinchin, you can protect your VM environment from disasters and cyber threats.
Share on:





