-
What is Xen?
-
What is VMware?
-
Xen vs. VMware
-
How to Choose?
-
Strategic migration between Xen and VMware with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
FAQs on the differences between Xen and VMware
-
Conclusion
Virtualization is a transformative technology that decouples software applications and operating systems from the underlying hardware, enabling them to operate as virtual entities. This not only reduces initial hardware investments and operational costs but also minimizes system outages, enhancing efficiency and resource optimization. Virtualization spans various domains such as data, desktop, and server virtualization. Among the top contenders in this space are Xen, backed by the Linux Foundation, and VMware, a leader in commercial virtualization solutions. If you're considering which platform best aligns with your organizational needs, this guide will delineate the distinctions and transition strategies between these two.
What is Xen?
Xen, backed by the Linux Foundation, is an open-source Type 1 hypervisor that enables concurrent execution of multiple operating systems on shared hardware. It leverages paravirtualization, optimizing performance by running modified guest operating systems, which communicate directly with the hypervisor, eliminating the need for extensive hardware emulation. This approach reduces the potential for security vulnerabilities. Xen also supports live migration of VMs across a LAN, facilitating load balancing and ensuring zero downtime during migrations. It is available in virtualization platforms like XCP-ng and Citrix Hypervisor (formerly XenServer).
What is VMware?
VMware, a leader in virtualization and cloud computing, offers a suite of proprietary technologies, including the enterprise-class Type 1 ESXi hypervisor. ESXi operates directly on server hardware, featuring its own kernel, and supports both paravirtualization and hardware-assisted virtualization. ESXi is unique in providing full virtualization capabilities. VMware's vCenter Server serves as a centralized management interface for orchestrating virtual machines and ESXi hosts in the vSphere environment, enabling features such as live migration of VMs and storage with vMotion. The vSphere platform comprehensively manages virtual machine infrastructure at scale, integrating ESXi and vCenter Server for streamlined administration.
Xen vs. VMware
| Xen | VMware | |
| Open source | Yes | No |
| Virtualization | Paravirtualization, hardware-assisted virtualization. | Paravirtualization, hardware-assisted virtualization, and full virtualization. |
| Supported OS | GNU/Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, MINIX, and Windows OS. | Windows, FreeBSD, Unix, Linux, macOS, Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian, Fedora, OS X, and others. |
| Thin provisioning | Yes | Yes |
| Dynamic resource allocation | No | Yes |
| Failover | No | Yes |
Asset management | Yes | No |
| Configuration mapping | Yes | No |
| Live migration | Yes | Yes |
| User-friendly Management | Easy | Complex for Windows users |
| Setup difficulty | Easy | Complex |
| Graphics support | Comprehensive | Limited |
| Host server management | Enterprise ready that has all capabilities to create and manage virtualization. | Custom grown that uses Busy Box to deliver a shell environment. |
| Storage types | NBD, GNBD, iSCSI, SATA, NFS, USB, etc. | FCoE and SSD for Swap; DAS, FC, and NAS storage. |
| Licensing fees | Free | Hefty |
| Technical support | White papers, email, brochures, blogs, booklet, instructional videos, telephone, forums, knowledge base, system upgrades, online self-service. | White papers, instructional videos, telephone, forums, knowledge base, system upgrades, online self-service, desk, remote training. |
| Audience | Personal, small, or medium businesses. | SMBs and large companies. |
How to Choose?
Choosing between Xen vs VMware hinges on your business size, needs, and budget. VMware, while offering a comprehensive suite of advanced features, comes with a higher price tag compared to Xen-based solutions like XenServer, Citrix Hypervisor, and XCP-ng. Although some advanced Xen features and editions, such as Citrix XenServer Enterprise and Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, require payment, the base Xen offerings remain cost-effective, making them appealing to many SMBs with tight budgets.
Additionally, consider the expertise of your IT staff and the compatibility of your IT environment. Xen-based virtualization is generally easier to manage, making it suitable for teams with limited virtualization experience. In contrast, VMware's extensive feature set comes with a steeper learning curve, necessitating more advanced IT skills. Ensure that your IT environment and staff capabilities align with the chosen platform to maximize efficiency and performance.
Strategic migration between Xen and VMware with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
Xen vs ESXi each offer distinct advantages, making them suitable for different organizational needs. If your business requirements change or if you need to leverage specific features from both platforms, migrating between them can be a strategic move. For such migration needs, using Vinchin Backup & Recovery is highly recommended.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional data protection solution designed to help organizations achieve reliable backups and fast V2V migrations in VM environments. Vinchi supports various virtualization platforms, VMware, Proxmox, Hyper-V, XenServer, XCP-ng, oVirt, RHV, etc. In addition, Vinchin offers an intuitive and user-friendly management interface, as well as powerful data protection and disaster recovery features. Whether it's a hardware failure, data loss, or unforeseen catastrophe, Vinchin enables users to quickly recover their VM environments and ensure the continuity of stable business operations.
To migrate a VMware VM to Xenserver using Vinchin as demonstrated below, follow the steps below:
1. Just select the backup of VMware VM
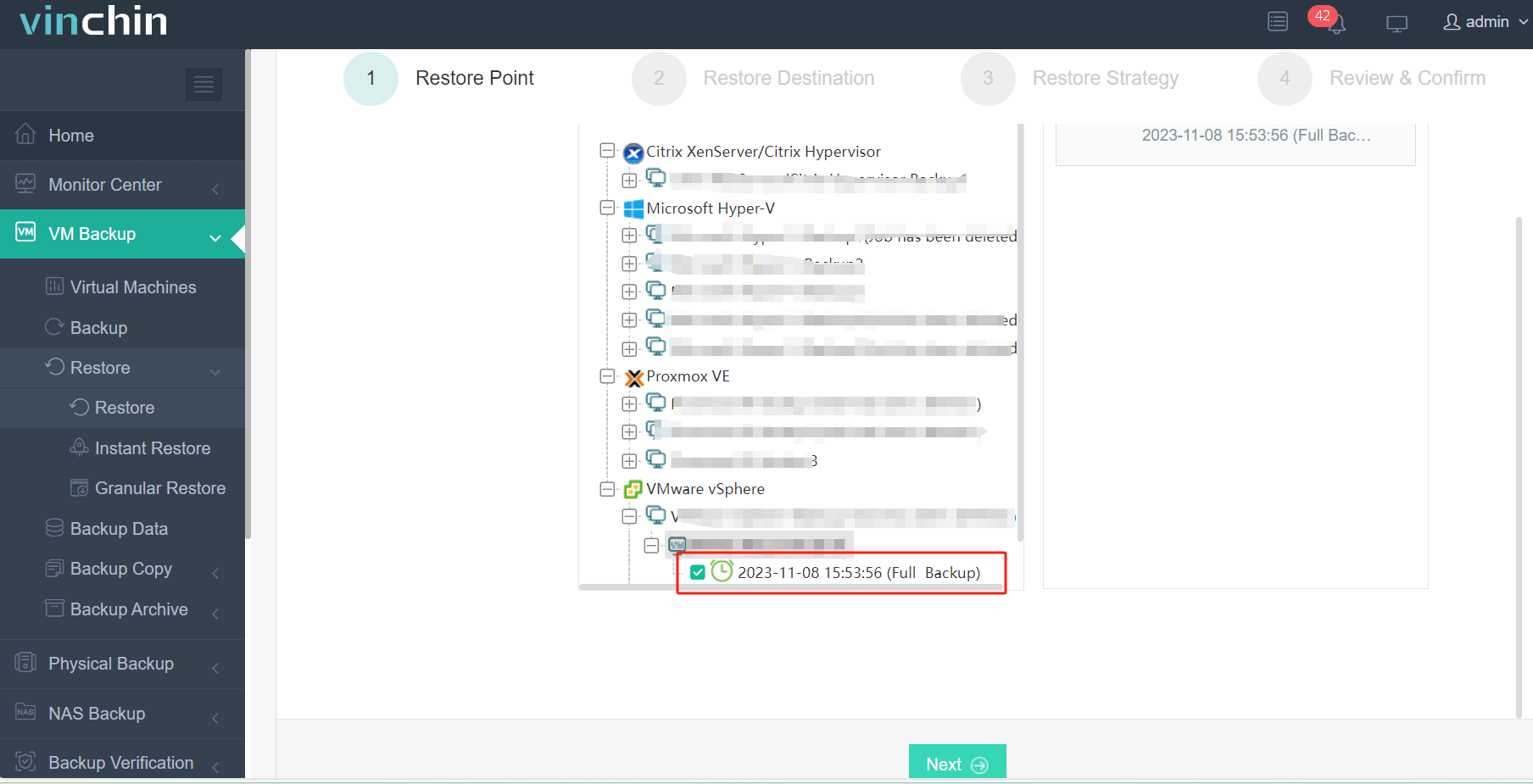
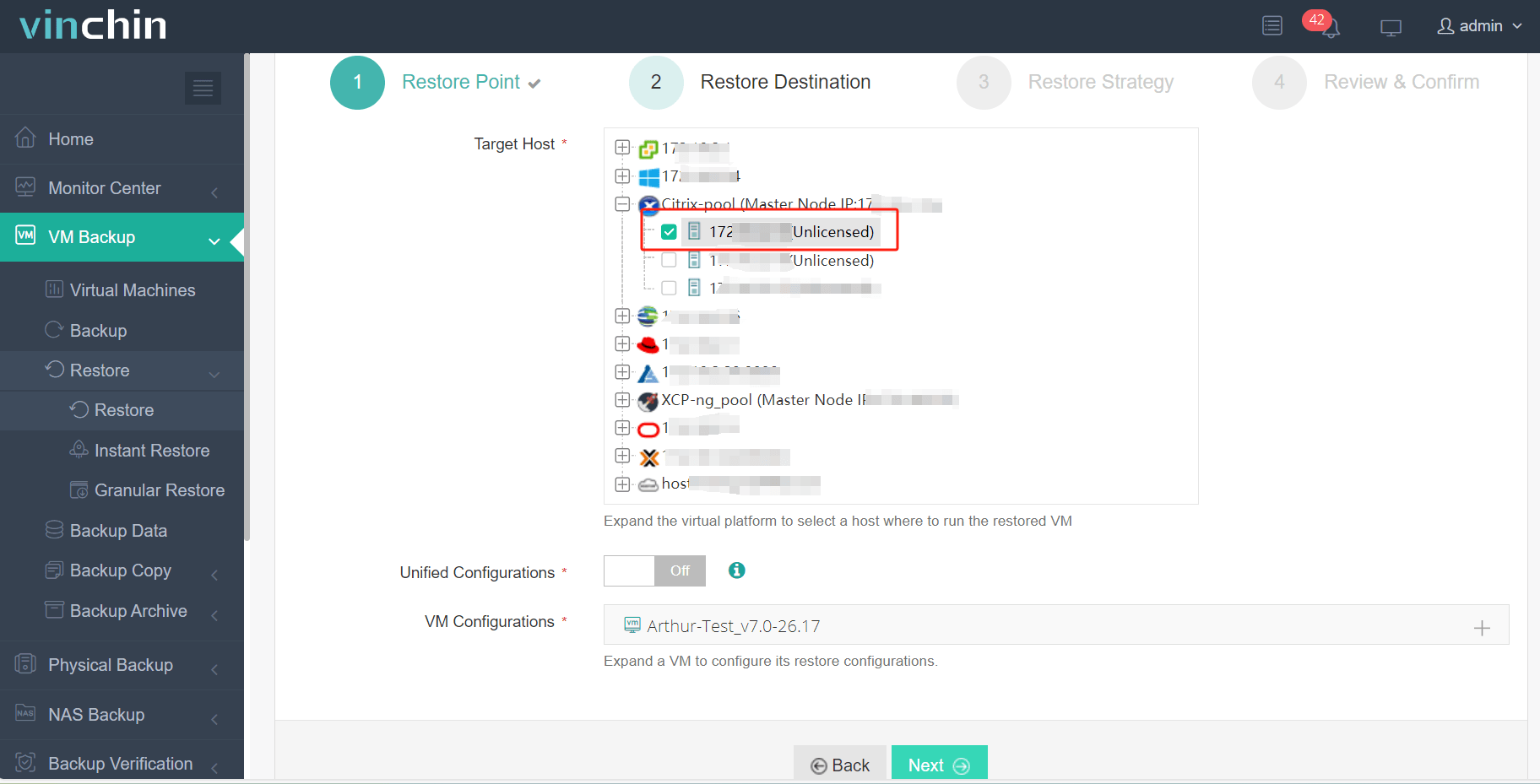
2. Select the Xenserver host as the target host
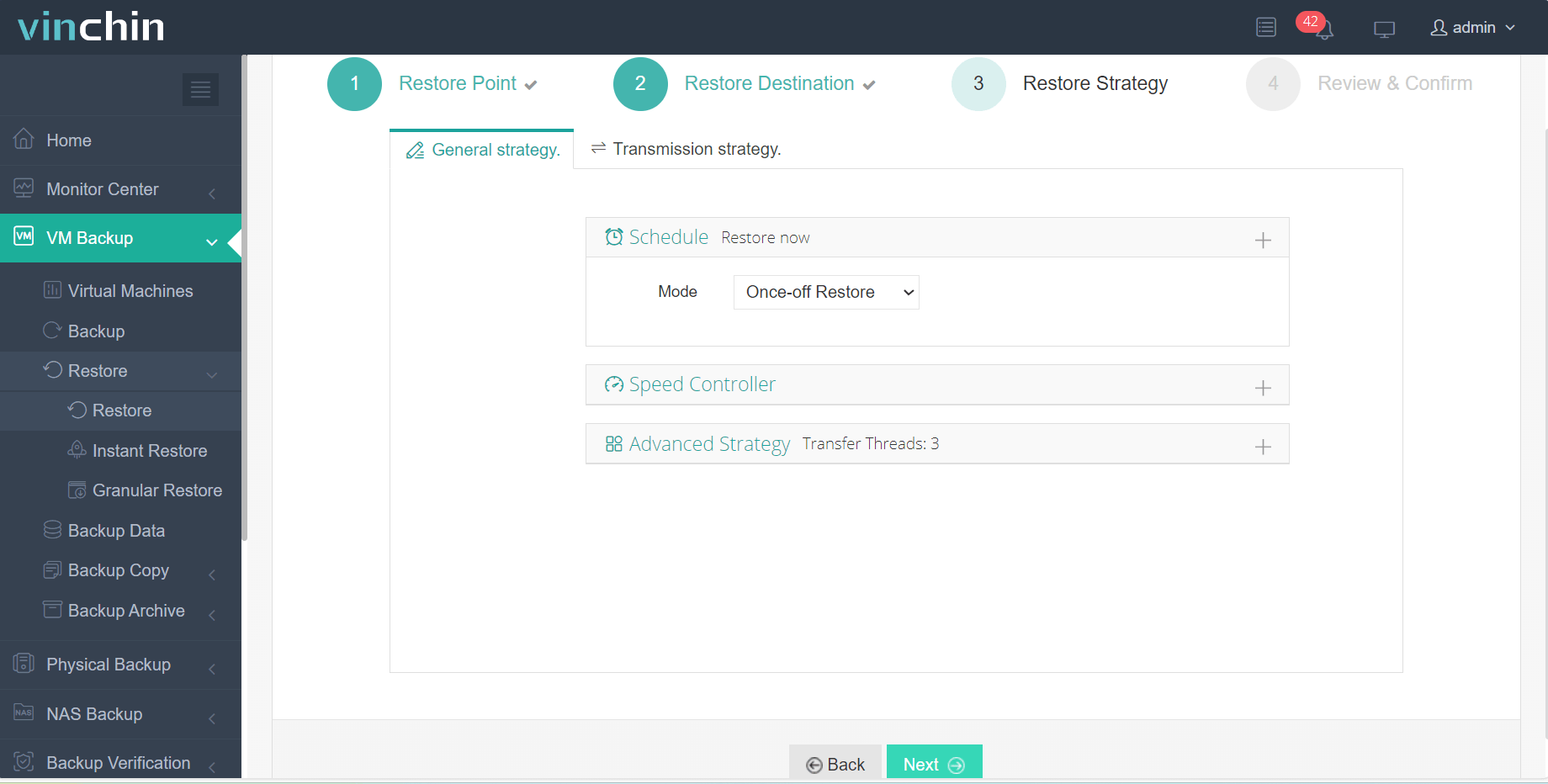
3. Select Once-off Restore
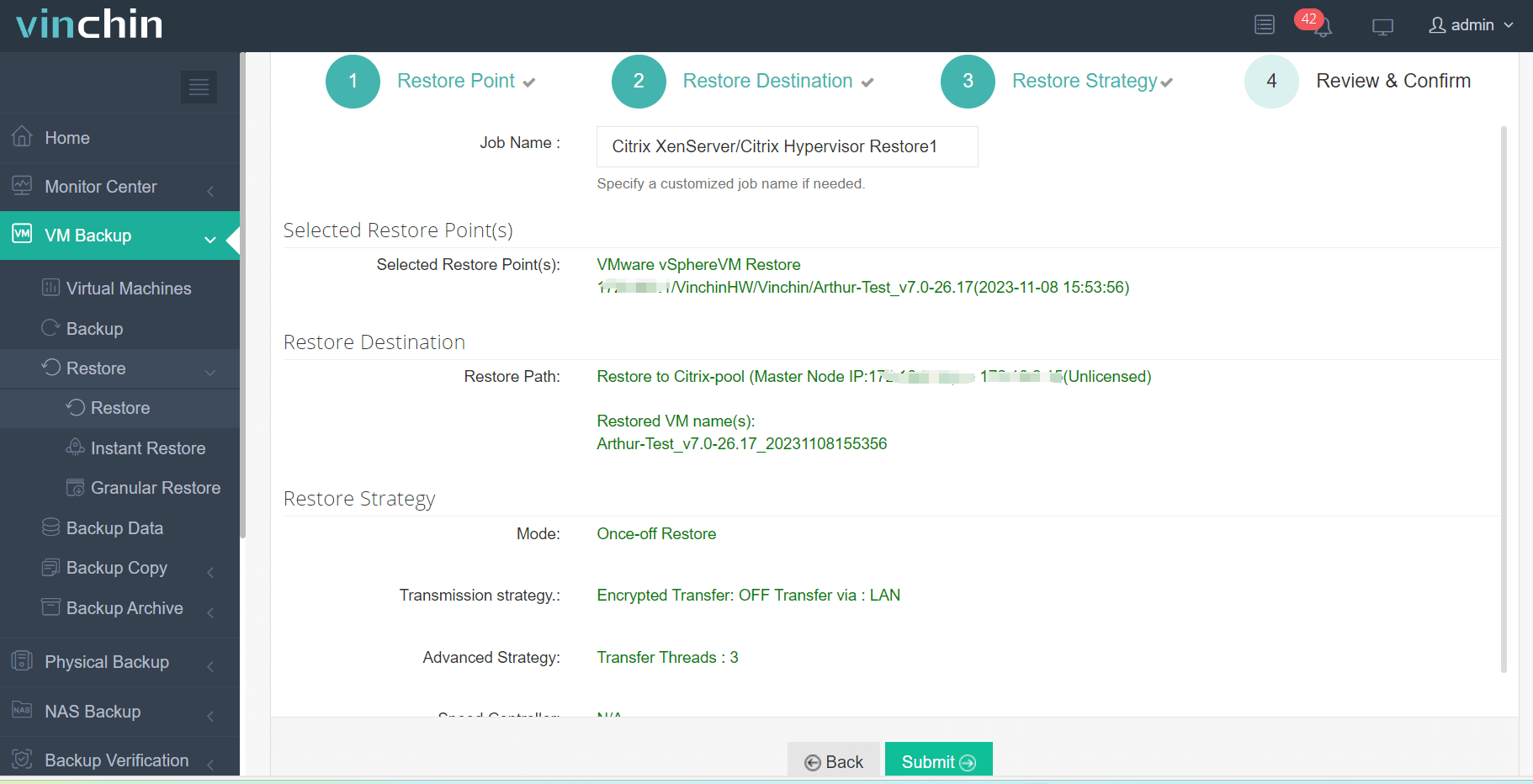
4. Submit the job
Vinchin offers a free 60-day trial for users to experience the functionality in a real-world environment. For more information, please contact Vinchin directly or contact our local partners.
FAQs on the differences between Xen and VMware
Q1: What are the management tools available for each?
A1: Xen: Managed through tools like XenCenter, Command Line Interface (CLI), and third-party solutions.
ESXi: Managed using VMware vSphere Client, vCenter Server, and CLI tools.
Q2: Can both hypervisors be used for cloud computing?
Xen: Widely used in cloud environments like AWS due to its scalability and flexibility.
ESXi: Commonly used in private clouds and supported by VMware's cloud solutions.
Conclusion
Xen and VMware each offer distinct advantages for virtualization, suitable for different organizational needs. For seamless migration between the two platforms, Vinchin Backup & Recovery is recommended, providing reliable backups, fast migrations, and robust data protection across various environments.
Share on:





