-
What Is KVM Cloud Computing?
-
Why Use KVM for Cloud Environments?
-
Security Hardening for KVM Environments
-
Optimizing Performance in KVM Cloud Computing
-
How to Deploy Private Clouds with KVM (OpenStack)?
-
Protecting Your Environment: Vinchin Backup & Recovery for KVM Virtual Machines
-
KVM cloud computing FAQs
-
Conclusion
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses use IT resources worldwide. Instead of relying on physical servers alone, organizations now run virtual machines (VMs) that maximize hardware efficiency and flexibility. At the core of this shift is KVM—a robust open-source technology that powers modern cloud environments across industries.
What Is KVM Cloud Computing?
KVM stands for Kernel-based Virtual Machine. It is a virtualization module built into the Linux kernel that turns any compatible Linux server into a hypervisor. With KVM, you can run multiple VMs—each with its own operating system—on one physical machine at the same time. This flexibility supports both Linux and Windows guests as well as other operating systems.
In kvm cloud computing setups, KVM acts as the engine behind private clouds in data centers and public clouds offered by major providers. Because it is open source and part of Linux itself, KVM enjoys wide adoption among enterprises seeking scalable solutions without vendor lock-in or high licensing costs.
Why Use KVM for Cloud Environments?
Many organizations choose kvm cloud computing because it offers clear benefits over traditional virtualization tools. First, being open source means there are no licensing fees—making it cost-effective whether you’re running ten VMs or thousands. Second, KVM delivers near-native performance by using hardware virtualization features like Intel VT-x or AMD-V; applications run fast with minimal overhead.
Security is another reason why IT teams trust KVM in their clouds. By leveraging built-in Linux security modules such as SELinux and sVirt, administrators can isolate VMs from each other and protect sensitive data from threats. Scalability comes naturally: you can start small then expand your environment as business needs grow—all while managing everything centrally.
Flexibility matters too: live migration lets you move running VMs between hosts without downtime; support for various storage backends means you can tailor infrastructure to fit unique requirements; integration with orchestration platforms like OpenStack makes automation possible at scale.
Major public clouds—including AWS and Google Cloud—use technologies based on or inspired by KVM to deliver reliable services globally.
Security Hardening for KVM Environments
Securing KVM cloud computing deployments requires careful planning beyond default settings. Start by enabling SELinux or AppArmor on your host systems; these mandatory access control frameworks help enforce strict isolation between VMs using sVirt integration within libvirt management tools.
Network isolation is also key: configure dedicated bridges or VLANs so VM traffic stays separate from management networks or other tenants’ workloads. Tools like firewalld or nftables allow fine-grained firewall rules around VM interfaces—reducing attack surfaces even further.
For added protection against firmware-level attacks, consider enabling Secure Boot using OVMF (Open Virtual Machine Firmware) when deploying UEFI-capable guest operating systems. Regularly update both host OS packages and QEMU/KVM binaries to patch vulnerabilities promptly—a simple but vital habit in any secure kvm cloud computing setup.
Optimizing Performance in KVM Cloud Computing
Performance tuning helps ensure that kvm cloud computing delivers consistent results under heavy load or mission-critical scenarios. Start with CPU pinning: assign specific vCPUs to physical CPU cores using libvirt XML configuration files so important workloads avoid contention during peak times.
Memory optimization comes next: enable huge pages on hosts handling memory-intensive applications; this reduces translation lookaside buffer (TLB) misses inside guest VMs and boosts throughput significantly (echo always > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled). For environments running many similar VMs side-by-side, activate Kernel Same-page Merging (KSM) by writing echo 1 > /sys/kernel/mm/ksm/run—this deduplicates identical memory blocks across guests automatically.
Storage I/O often becomes a bottleneck if left unchecked; use VirtIO drivers inside guest operating systems whenever possible—they provide paravirtualized disk/network interfaces optimized specifically for virtualized workloads. Monitor disk latency regularly using iostat or collectd plugins so you can spot issues early before they impact users downstream.
How to Deploy Private Clouds with KVM (OpenStack)?
Private clouds offer full control over data residency and compliance while delivering self-service agility internally—and OpenStack remains one of the most popular platforms built atop kvm cloud computing principles today.
Install required packages:
sudo apt-get install qemu-kvm libvirt-daemon-system libvirt-clients bridge-utils virt-manager
This command sets up both hypervisor components plus basic management utilities needed later on.
Deploy OpenStack next—either manually following official guides tailored per distribution or using production-ready automation tools like MicroStack/Kolla-Ansible if scaling out quickly matters more than granular customization right away. During controller node configuration steps select “KVM” under compute driver settings within Nova’s config files (nova.conf).
Once operational log into Horizon Dashboard via browser; navigate through Project, then Instances, finally click Launch Instance button after filling out image/flavor/network fields accordingly—the rest happens automatically thanks to tight integration between OpenStack APIs & underlying kvm cloud computing stack!
Scale horizontally anytime simply by adding more compute nodes registered against central controller(s); manage quotas/policies centrally without ever touching individual hosts again unless troubleshooting rare edge cases directly at CLI level becomes necessary someday down road.
Protecting Your Environment: Vinchin Backup & Recovery for KVM Virtual Machines
Reliable backup is critical in any virtualized environment, especially when managing complex infrastructures powered by kvm cloud computing. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as an enterprise-grade solution designed specifically for professional VM backup needs across more than 15 mainstream virtualization platforms—including Proxmox, VMware, Hyper-V, oVirt, OLVM, RHV, XCP-ng, XenServer, ZStack, OpenStack, among others—with comprehensive support for KVM environments such as Proxmox and oVirt prioritized here due to their relevance in this context.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers advanced features including forever-incremental backup strategies for efficient storage utilization; LAN-free backup options that minimize network load during operations; granular restore capabilities allowing precise file-level recovery; robust data deduplication/compression mechanisms optimizing space usage; and instant recovery functions that rapidly restore service continuity after failures—all contributing to streamlined protection of mission-critical workloads.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding your environment straightforward:
Step 1: Select the Proxmox VM (or relevant hypervisor’s VM) you wish to back up.
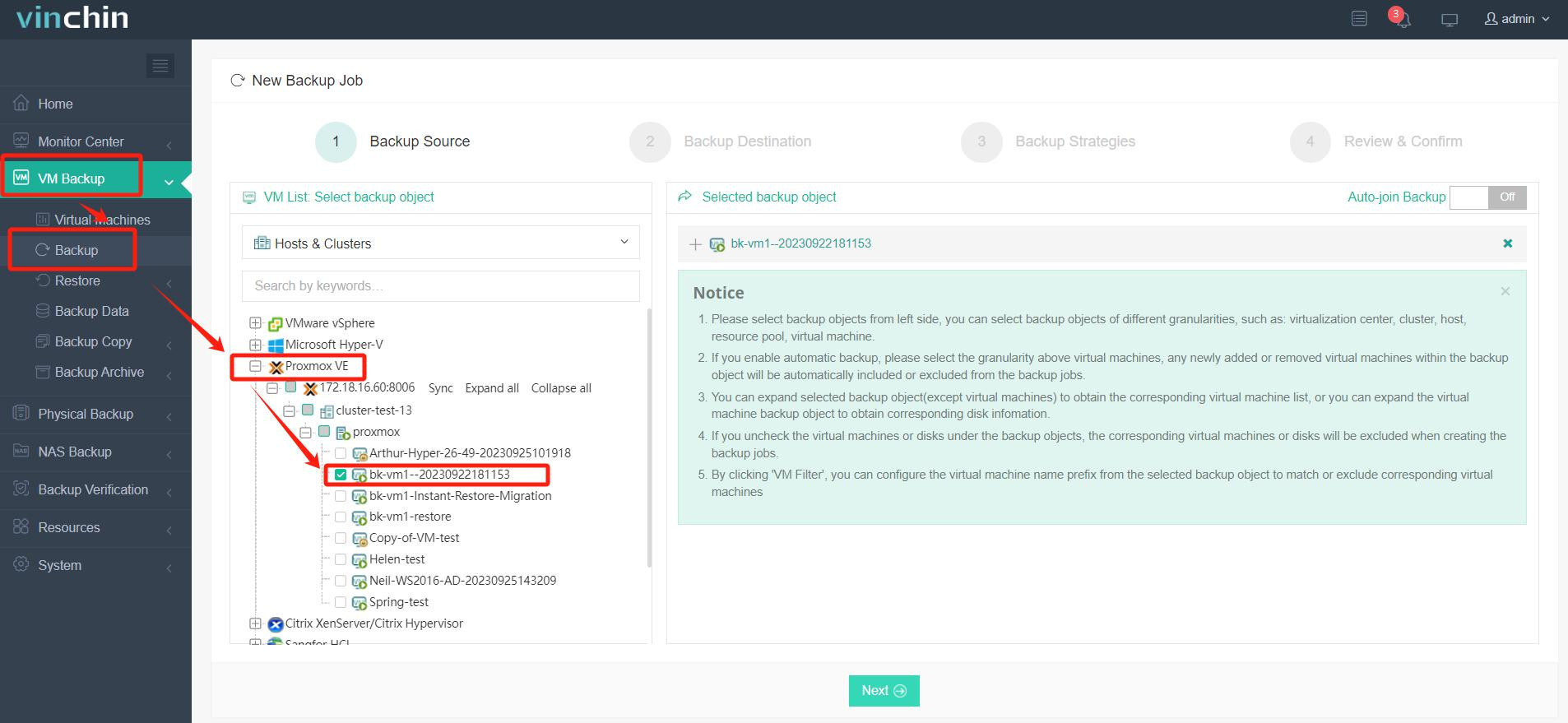
Step 2: Choose your preferred backup storage location.
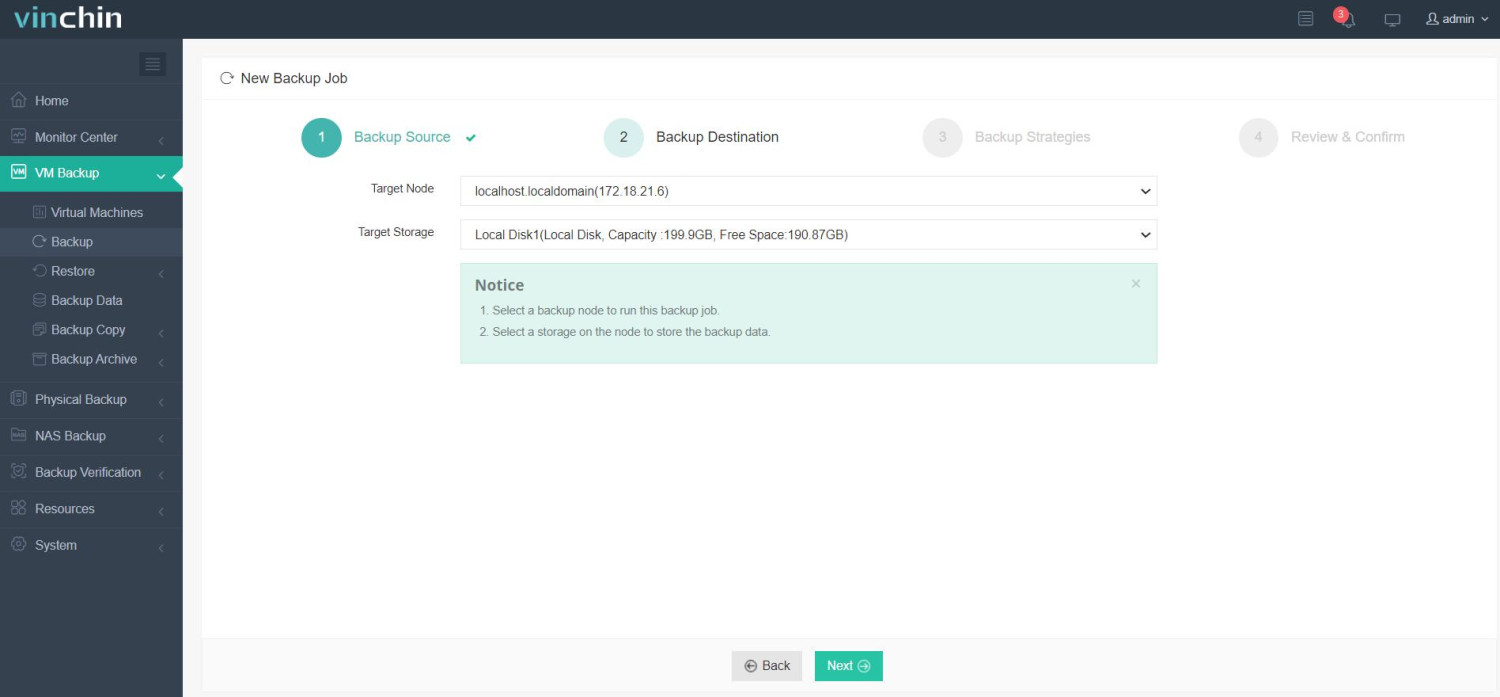
Step 3: Configure an appropriate backup strategy tailored to organizational policies.
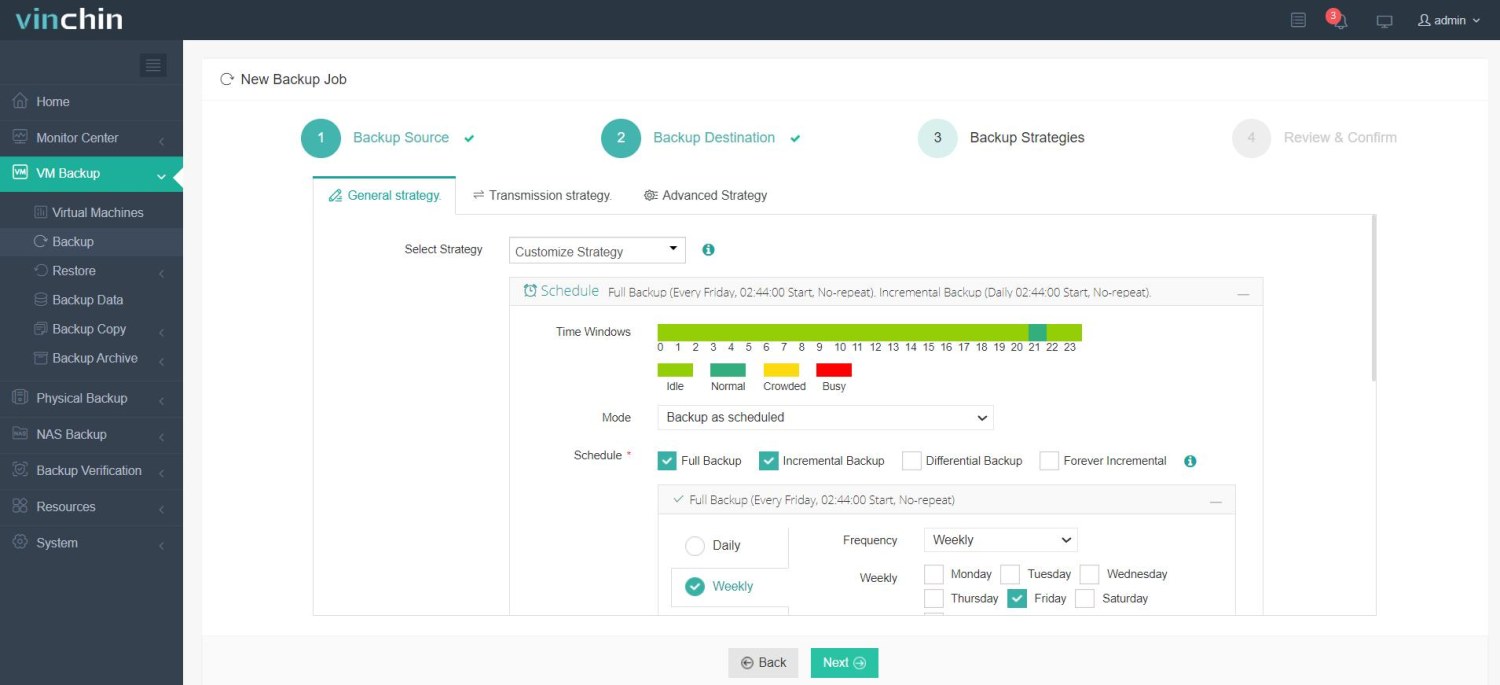
Step 4: Submit the job—your backups will proceed automatically.
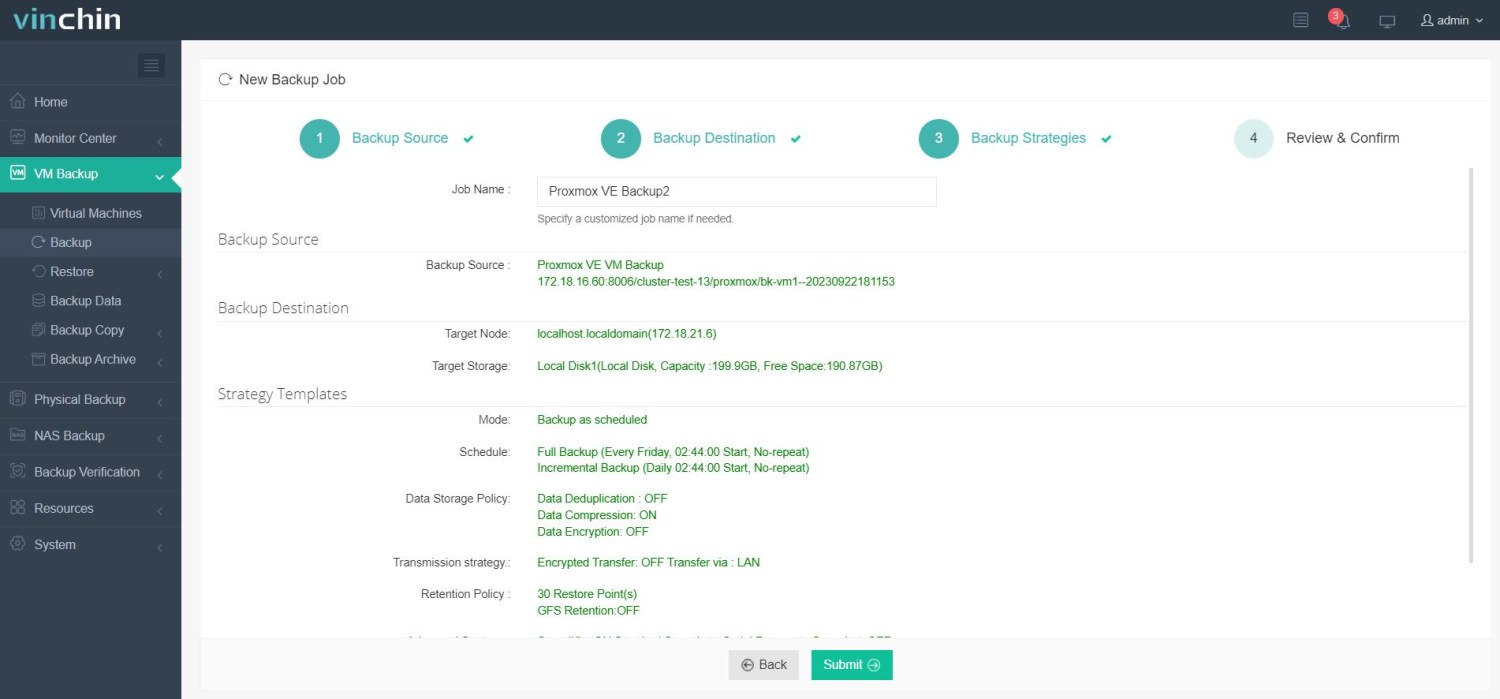
Trusted globally by thousands of enterprises and highly rated in independent reviews, Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a 60-day full-featured free trial—click below to experience comprehensive enterprise data protection firsthand!
KVM cloud computing FAQs
Q1: Can I use live migration between different hardware generations?
A1: Yes—with compatible CPUs/settings enabled—but test thoroughly since mismatches may cause failures during migration events occasionally observed rarely still sometimes nonetheless.
Q2: What are best practices for monitoring resource usage in large-scale deployments?
A2: Deploy centralized monitoring solutions collecting metrics/logs from all hosts regularly visualizing trends/issues proactively preventing outages efficiently always ideally.
Q3: How does resource overcommitment work in kvm cloud computing?
A3: You can allocate more vCPUs/RAM than physically present but monitor closely using tools like virt-top/KSM since excessive overcommit risks performance degradation/stability problems potentially arising unexpectedly otherwise.
Conclusion
KVm cloud computing empowers IT teams worldwide with unmatched flexibility, scalability, and security across private/public/hybrid scenarios alike today already everywhere practically speaking! For reliable backup/migration needs involving critical virtual machines trust Vinchin—it keeps your environment safe no matter what tomorrow brings next!
Share on:










