-
What's new in vCenter 8?
-
How to backup VM in vCenter with Vinchin?
-
vCenter 8 FAQs
-
Conclusion
vCenter Server sits at the core of VMware’s software-defined data center. It unifies management of ESXi hosts, virtual machines, storage, and networking through a single interface. Version 8 advances this role with faster updates, deeper lifecycle automation, and broader support for modern hardware and containers. In this article, we’ll explore each new capability in detail, then show you how to protect your workloads, answer common vCenter 8 questions, and wrap up with best-practice guidance.
What's new in vCenter 8?
vCenter 8 focuses on reducing downtime, automating lifecycle tasks, offloading work to DPUs, integrating Kubernetes services, and scaling to larger environments.
Update & Patch Management Redefined
vCenter Reduced Downtime Update lets administrators apply patches or upgrades with minimal impact. Instead of taking the entire service offline, it triggers an automatic switchover between active and passive nodes in an HA cluster, shrinking maintenance windows to roughly 2–5 minutes even in linked-mode or self-managed topologies.
Enhanced Lifecycle Management
vSphere Lifecycle Manager (vLCM) now offers both image-based and baseline-based workflows. Image-based cluster management means you build a custom ESXi image—choosing base OS, vendor add-ons, and optional components like the VMware Host Client—then apply it uniformly across hosts. Baseline-based management remains available for admins preferring bulletins and patch remediation.
Hardware Offload with Dual DPU Support
As data centers adopt SmartNICs and DPUs, vCenter 8 extends vLCM to manage dual-DPU configurations. You can remediate both the host and its attached DPUs in lockstep, preserving consistency across firmware and driver versions for offload-heavy workloads.
Container Services & Tanzu Integration
vCenter 8 deepens vSphere with Tanzu support by integrating updated Kubernetes management directly into the UI. Administrators gain access to Cluster API enhancements, Workload Availability Zones for isolating mission-critical services, and an independent TKG (Tanzu Kubernetes Grid) service that decouples Kubernetes releases from vSphere lifecycles. This separation lets you adopt upstream Kubernetes features on your schedule.
Performance & Scale Improvements
Under the hood, vCenter 8 raises configuration maximums to accommodate larger data centers. ESXi hosts can now support up to 1,024 VMs and 4,096 vCPUs per host. Total VMs per vCenter instance climb from 8,000 to 10,000, and hosts per vLCM image-managed cluster jump from 400 to 1,000. The vSphere Client service’s heap size and performance profiles have also been tuned for responsiveness in heavy-load scenarios.
NFS nConnect & Storage Optimizations
vCenter 8 Update 3 adds support for NFS v4.1 nConnect, which enables multiple TCP connections per datastore mount point to boost throughput and provide path redundancy. This feature is especially valuable for large VM clusters and storage arrays serving high-IOPS workloads.
How to backup VM in vCenter with Vinchin?
Now, let’s look at enterprise-grade VM protection. Vinchin is a professional, enterprise-level backup solution for VMs on over 15 other platforms—including VMware Hyper-V, Proxmox, oVirt, OLVM, RHV, XCP-ng, XenServer, OpenStack, and ZStack.
Vinchin covers every backup scenario: full backup, incremental backup, forever-incremental backup, differential backup, scheduled and repetitive backup, plus data deduplication and compression to cut storage costs. You get V2V migration for seamless hypervisor conversions, multi-thread transmission for faster transfers, and throttling policies to avoid network congestion. Other perks include GFS retention, CBT support, quiesced snapshots and HotAdd for VMware, SpeedKit acceleration, LAN-free backup, data encryption, VM backup data verification, instant recovery (all but Hyper-V), granular restore, and cloud/tape archiving—yet this list barely scratches the surface.
Vinchin’s web console is simple and clear. To back up a VM in vCenter 8, you follow four steps tied to your specific VM:
1. Select the VM to backup from the Virtual Machines list.
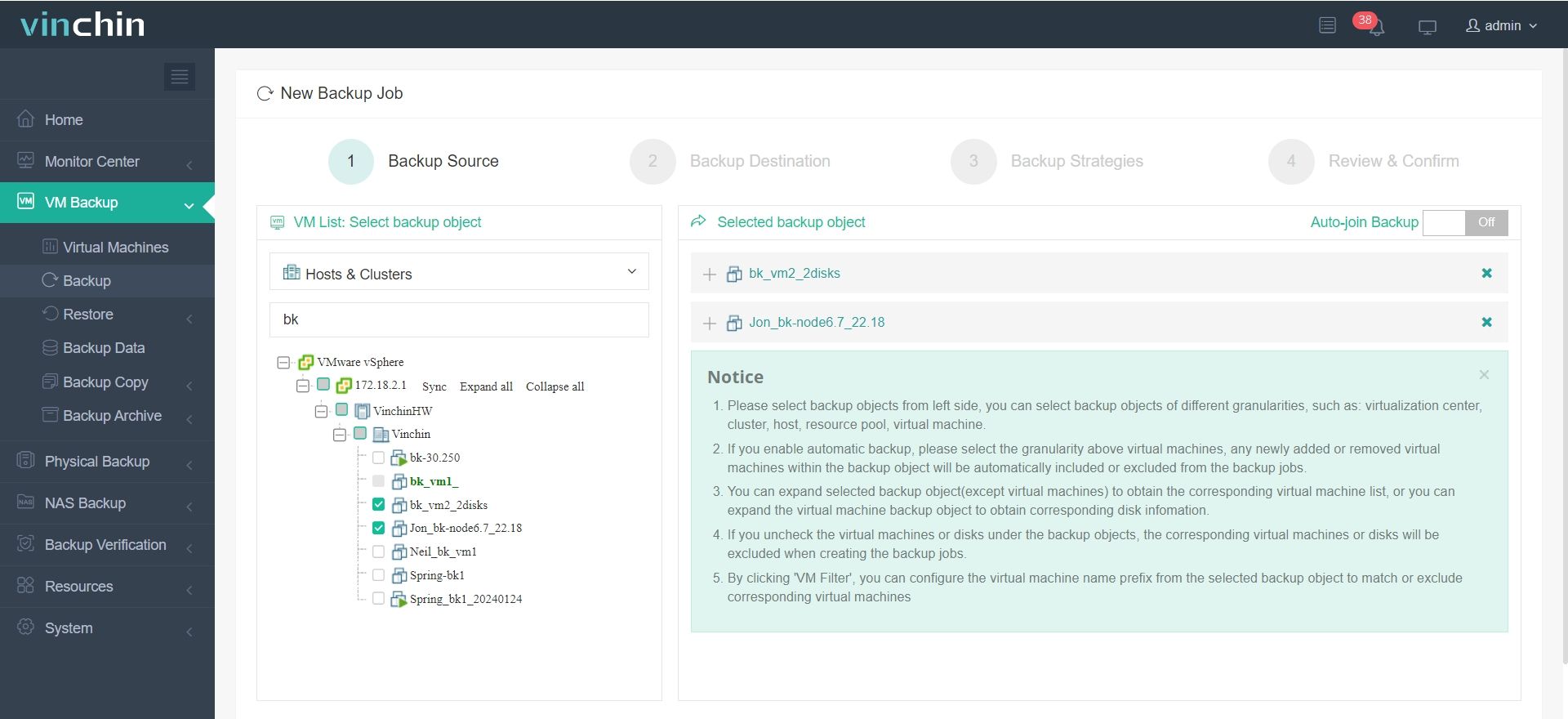
2. Choose backup storage by picking or adding a repository under Backup Destination.
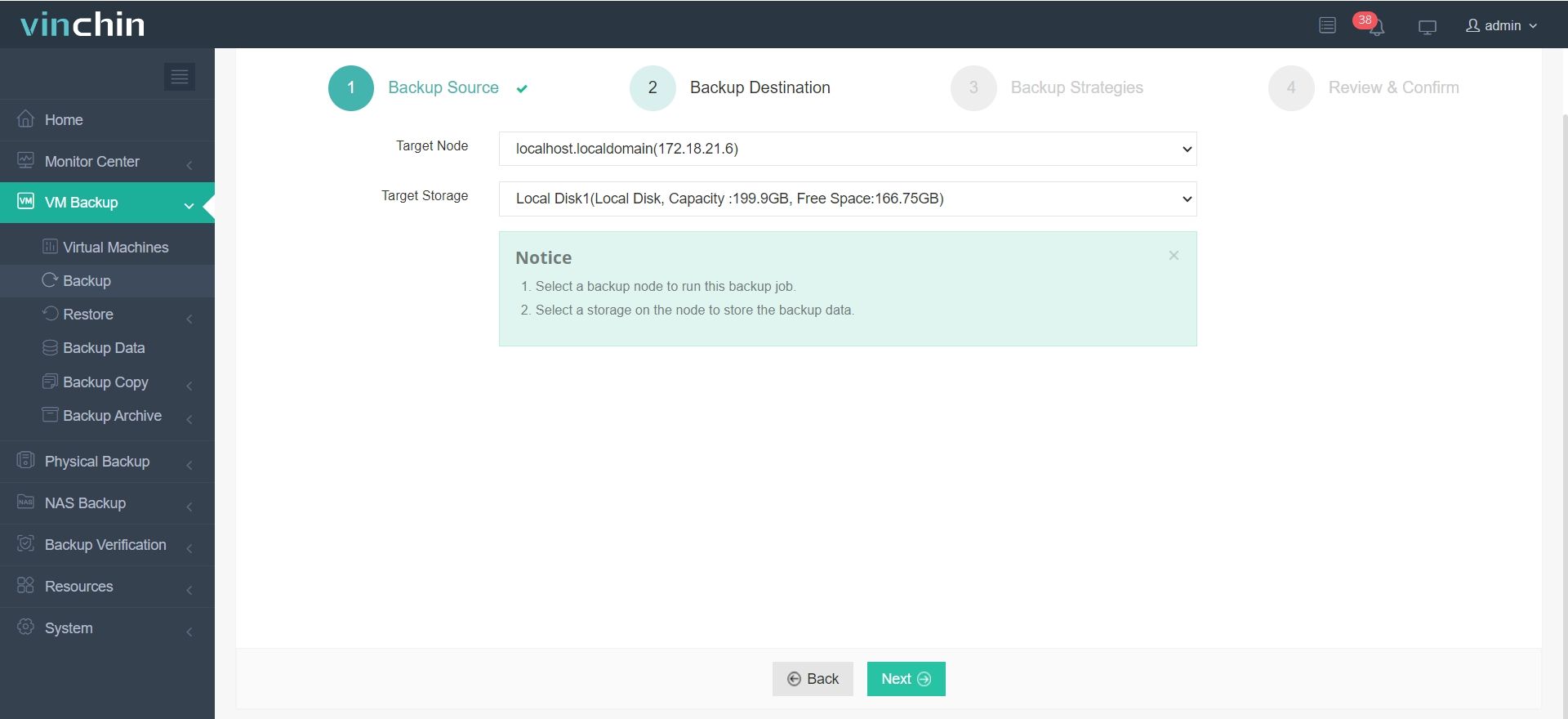
3. Select backup strategies—define schedule, GFS retention, and throttle rules in Backup Strategies.
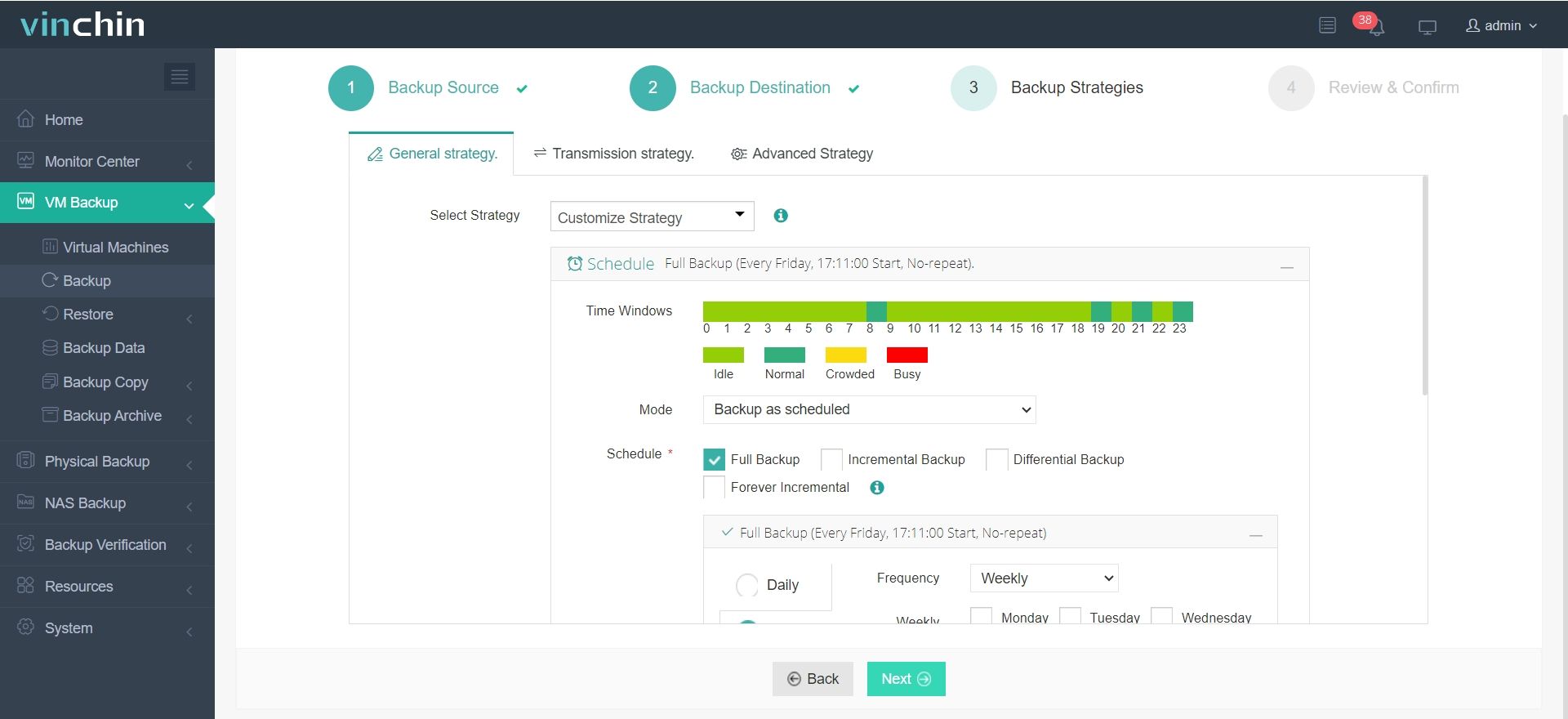
4. Submit the job by clicking Submit;
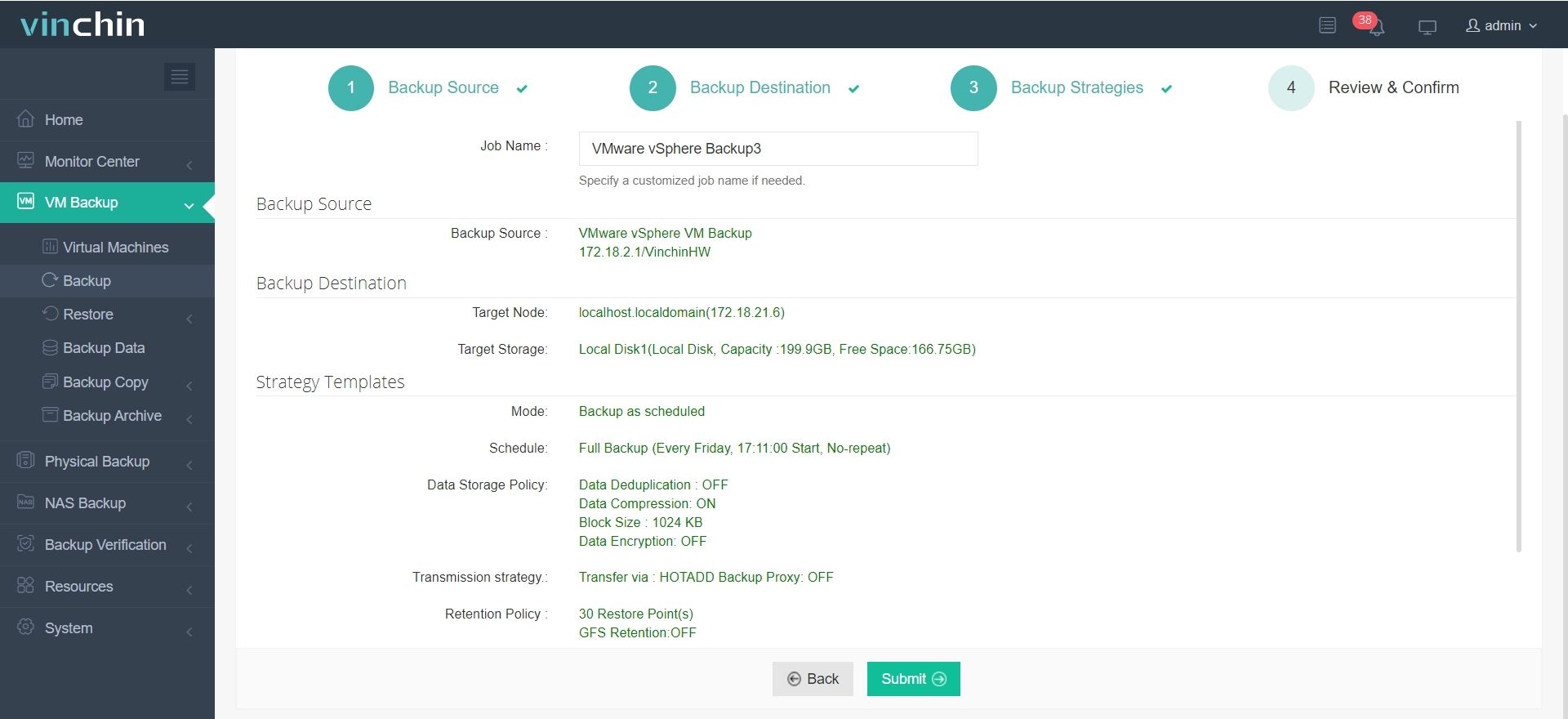
Vinchin is trusted by thousands of enterprises worldwide and earns top ratings for reliability and ease of use. Try it free for 60 days—click DOWNLOAD to deploy in minutes.
vCenter 8 FAQs
Q1: How do I configure an off-peak Reduced Downtime Update window?
Use Update Manager settings to schedule the switchover during low-usage hours, then monitor progress in Monitor > Update Manager > Baselines and Patches.
Q2: Can I roll back a vLCM image remediation?
Yes—navigate to vSphere Lifecycle Manager > Desired Images, select the previous image version, and click Rollback.
Q3: What NFS protocols does vCenter 8 support?
vCenter supports NFS v3 and v4.1, with nConnect multiple-TCP support on v4.1 for improved throughput.
Q4: Which VMs are excluded from live patching?
Fault Tolerance VMs, DirectPath I/O VMs, and vSphere Pods require manual remediation—live patch only applies to standard ESXi hosts.
Q5: How large are typical appliance backups?
Full VCSA backups typically range from 2–5 GB; enabling deduplication and compression can cut storage by up to 50 percent.
Conclusion
vCenter 8 streamlines lifecycle operations, supports modern offload hardware, and scales to thousands of workloads. By combining its built-in innovations with Vinchin’s feature-rich backup and instant recovery, administrators can maximize uptime and safeguard virtual infrastructures.
Share on:






