-
What is vmnet0?
-
What is vmnet1?
-
What is vmnet8?
-
How to backup VMware virtual machines?
-
Vmnet FAQs
-
Conclusion
VMware virtual networks (vmnets) are software-defined switches that enable precise network segmentation for VMs. Understanding vmnet0 (bridged), vmnet1 (host-only), and vmnet8 (NAT) is critical for designing secure, high-performance environments. This guide covers architectural principles, configuration scenarios on both Workstation Pro and ESXi, and enterprise-grade use cases for production and lab setups.
What is vmnet0?
vmnet0 is actually a virtual bridge. This bridge has many ports. One port is used to connect to your Host, and one port is used to connect to your virtual machine. Their locations are equal, so in Bridged mode, you can make the virtual machine a machine with the same status as your Host.
What is vmnet1?
vmnet1 presents as Host-Only network mode, which is used to establish an isolated network environment, where vmnet1 is also a virtual switch, one port of the switch is connected to your Host, and the other port is connected To the virtual DHCP server (actually a component of vmware), the remaining port is connected to the virtual machine. The virtual network card "VMWare Virtual Ethernet Adapter for VMnet1" serves as the gateway interface of the virtual machine and provides services for the virtual machine.
After the virtual machine is started, if you use the ipconfig command, you will clearly see that your default gateway is pointing to the address of the "VMWare Virtual Ethernet Adapter for VMnet1" network card. (In fact, it does not provide routing. This is designed by VMware. It does some things besides providing routing—in fact, I don’t know what it does.) There is no routing provided here. The main manifestation is No NAT service is provided, so that virtual machines cannot access addresses outside the network segment specified in Host-Only mode.
What is vmnet8?
vmnet8 uses NAT, the simplest networking method, from the host's "VMWare Virtual Ethernet Adapter for VMnet8" virtual network card, connected to the vmnet8 virtual switch, the other port of the virtual switch is connected to the virtual NAT server ( This is also a Vmware component), and one port is connected to the virtual DHCP server, and the other ports are connected to the virtual machine.
The gateway of the virtual machine is the machine where the "VMWare Virtual Ethernet Adapter for VMnet8" network card is located. Nonsense, this must be yours Host machine. Similarly, you can also see with ipconfig that the default gateway of your virtual machine also points to your "VMWare Virtual Ethernet Adapter for VMnet8" virtual network card address. In contrast, it can be seen that the difference between the NAT networking mode and the Host-Only mode is whether there is an additional NAT service.
How to backup VMware virtual machines?
Before diving back into networking, consider how you’ll protect your VMs. Vinchin is a professional, enterprise-level VM backup solution supporting VMware, Hyper-V, Proxmox, oVirt, OLVM, RHV, XCP-ng, XenServer, OpenStack, ZStack, and 15+ other platforms.
It offers full, incremental, forever-incremental, differential, scheduled, and repetitive backups, plus data deduplication and compression. You’ll find V2V migration, throttling policy, GFS retention, quiesced snapshots, HotAdd, CBT, LAN-free backup where supported, encryption, multi-thread transmission, backup data verification, instant recovery (all but Hyper-V), granular restore, and cloud/tape archiving, yet these are just a sample of its rich feature set.
Backing up VMs via Vinchin’s web console takes four clicks:
1. Select the VMware VM you need to protect;
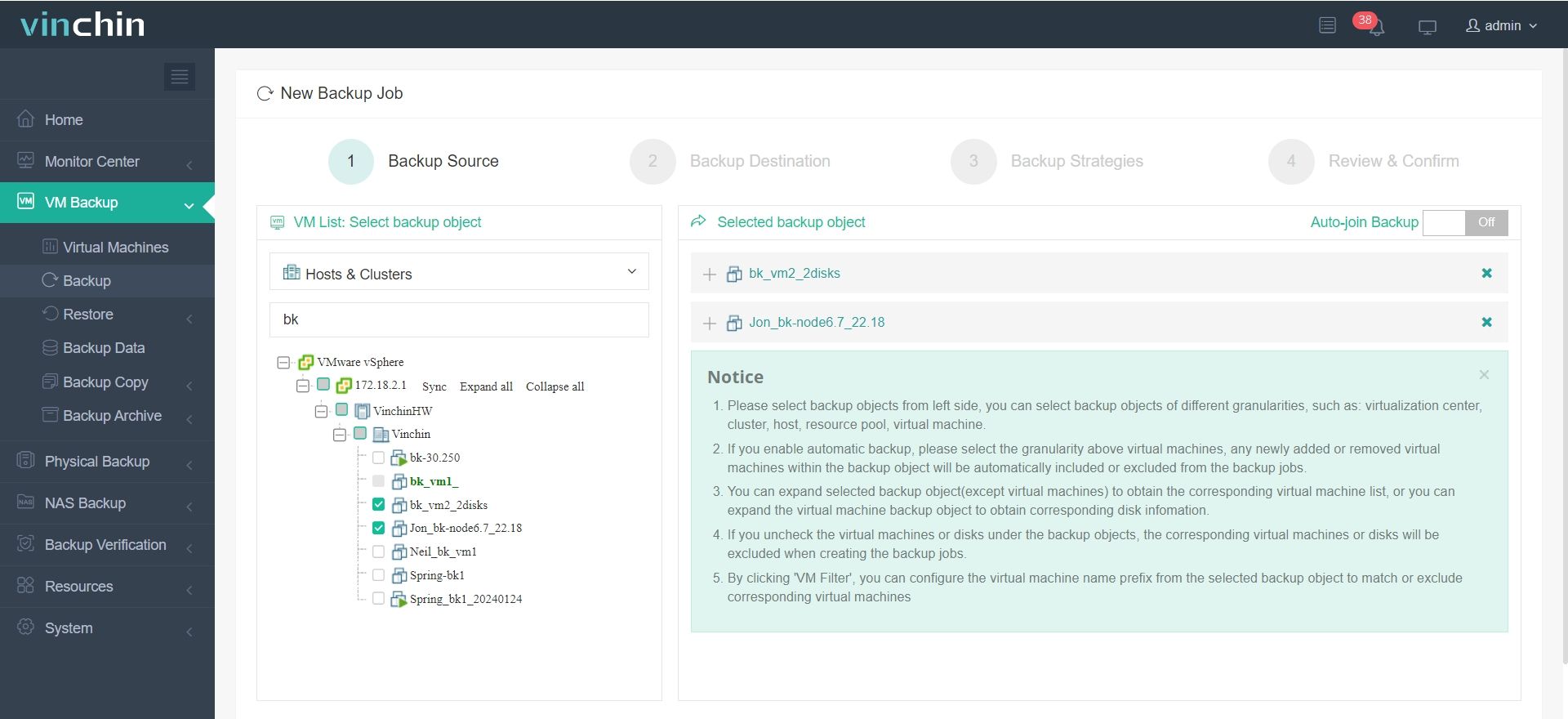
2. Choose your backup storage repository;
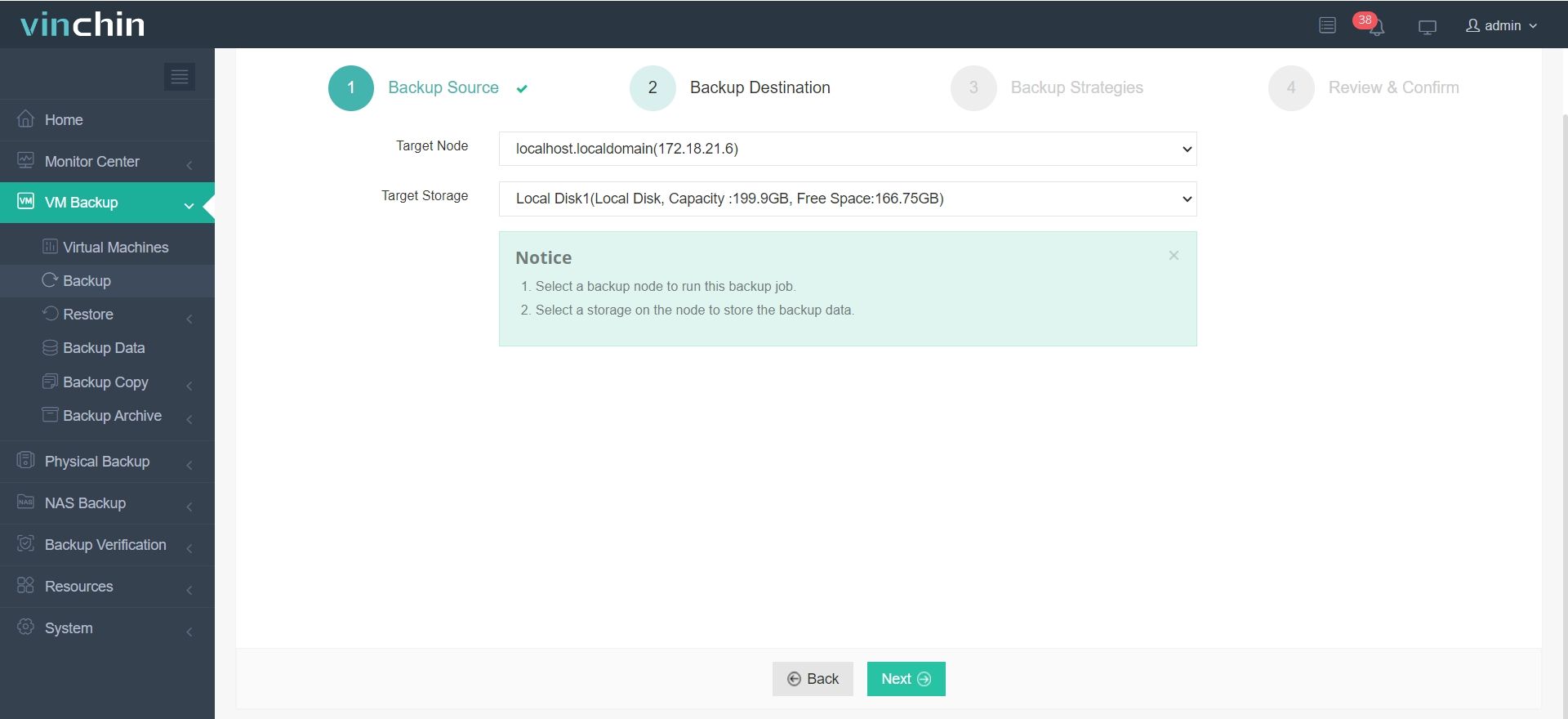
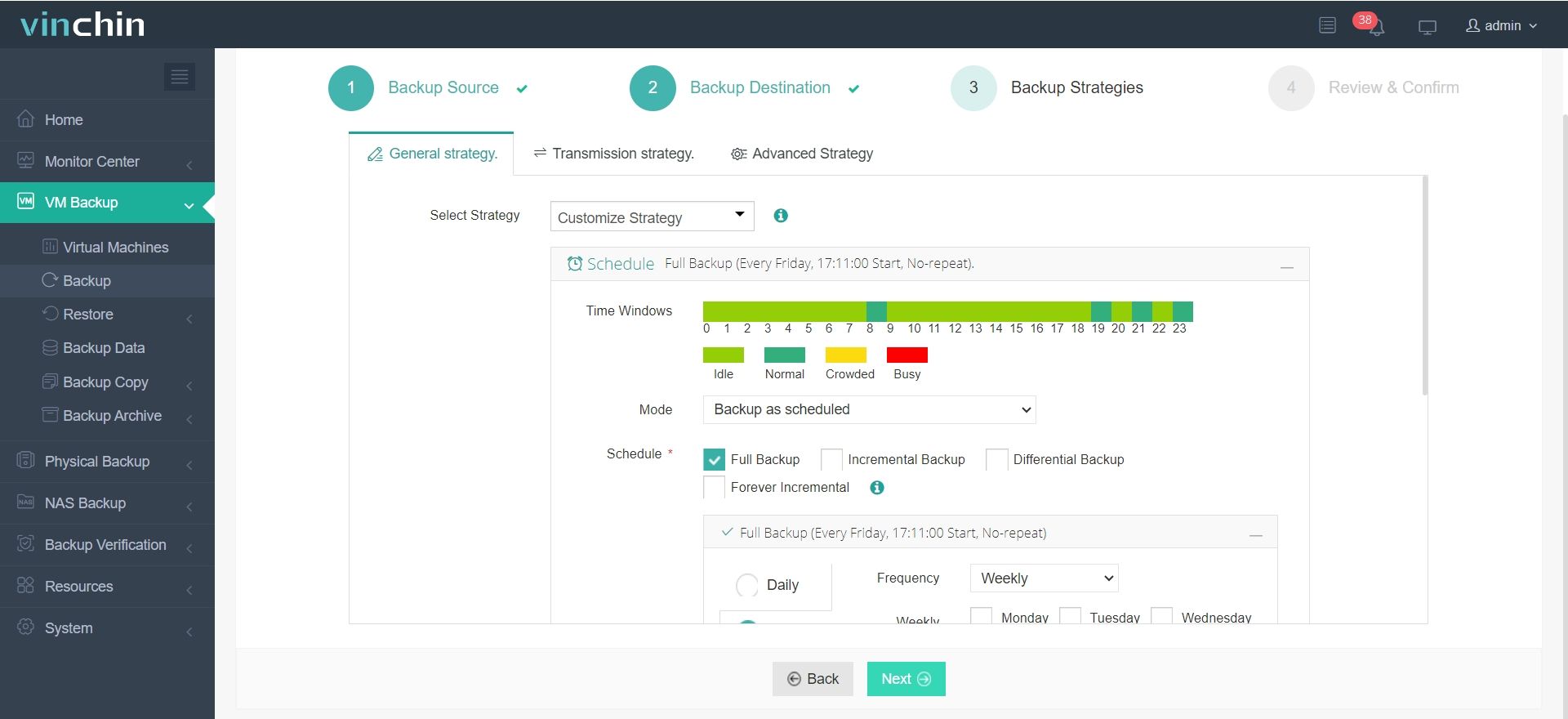
3. Pick your strategies—full, incremental, forever-incremental, etc.
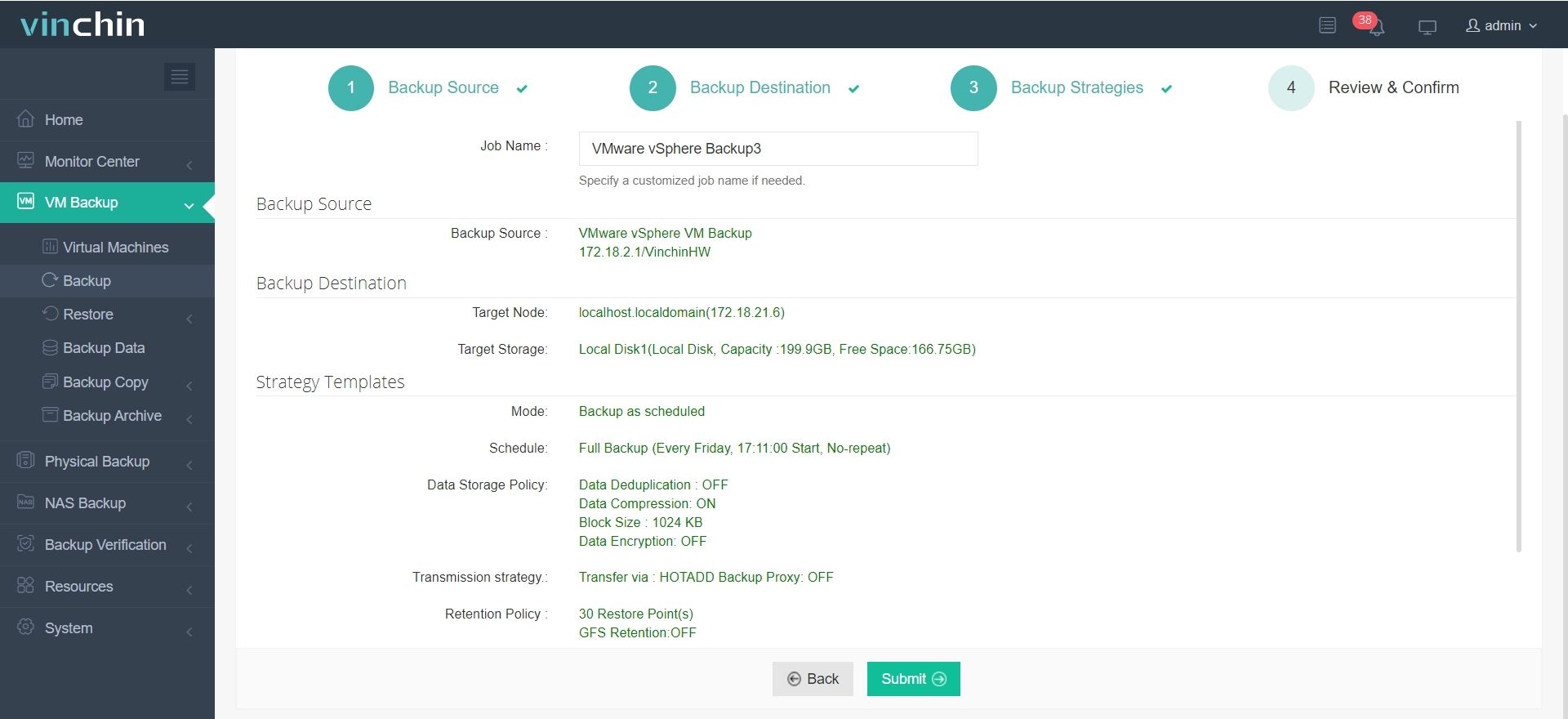
4. Submit the job and monitor progress.
With customers worldwide and top industry ratings, Vinchin offers a 60-day full-featured free trial. Ready to secure your VMware workloads? Download Installer and deploy in minutes.
Vmnet FAQs
Q1. How can I troubleshoot bridged DHCP failures on vmnet0?
Capture packets on vmnet0 with tcpdump -i vmnet0 to verify DHCP discover and offer messages, and check switch port security for MAC filtering.
Q2. Can I interconnect multiple host-only subnets like vmnet1 and vmnet2?
Deploy a virtual router (for example, a pfSense VM) attached to each vmnet, or configure static routes on your host OS to route between subnets.
Q3. How do I expose a service running on a NAT VM through vmnet8?
In Virtual Network Editor, choose VMnet8, open NAT Settings, add a forwarding rule mapping Host Port to Guest IP:Port, then restart the VM’s network service.
Q4. How do vmnets affect VM performance?
Bridged mode offers near-native throughput, limited only by physical NIC capacity; NAT and host-only incur under 2 ms extra latency—mitigate by using vmxnet3 adapters and adequate vCPU allocation.
Conclusion
Mastering VMware vmnets lets you craft network architectures tailored to performance, isolation, and security needs. Use bridged networks for critical production VMs, host-only for sandboxed or backup channels, and NAT for controlled internet access. Combine these with vSphere Distributed Switches or bonded adapters for centralized management and resilience. Always validate your setup by capturing traffic on both host and guest interfaces to confirm packet flows.
Share on:





