-
What Are AWS EC2 Instance Types and Sizes?
-
How to Choose the Right EC2 Instance Size?
-
Comparing Popular EC2 Instance Families & Sizes
-
Vinchin Backup Solutions for Modern Virtual Infrastructures
-
AWS EC2 Sizes FAQs
-
Conclusion
AWS EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) powers much of today's cloud infrastructure. With hundreds of instance types and sizes available, picking the right one can feel overwhelming. This guide will help you understand AWS EC2 sizes from basic concepts to advanced selection strategies. We'll walk through how instances are structured, how to choose wisely for your workloads, compare popular options—including new generations—and explain how to protect your data with Vinchin.
What Are AWS EC2 Instance Types and Sizes?
AWS EC2 offers virtual machines called instances that run your applications in the cloud. Each instance type targets a specific use case—some focus on balanced resources while others specialize in compute power or memory capacity.
AWS EC2 Instance Types
Instance types group together hardware profiles optimized for different tasks:
General Purpose: These balance CPU, memory, and networking (like M or T families). They suit web servers or small databases.
Compute Optimized: Designed for high CPU performance (C family). Ideal for scientific computing or batch processing.
Memory Optimized: Offer large RAM amounts (R, X, U families). Best for analytics or in-memory databases.
Storage Optimized: Provide fast disk throughput (I, D, H families). Useful for NOSQL databases or large-scale data analytics.
Accelerated Computing: Feature GPUs or FPGAs (P, G, F families) for machine learning or graphics-intensive tasks.
Each family has multiple generations—newer ones often deliver better price/performance ratios.
Decoding Instance Sizes
Within each type are several sizes: nano, micro, small, medium, large—and up to 24xlarge or even metal (bare metal access). For example:
The M5 family ranges from m5.large (2 vCPUs/8 GiB RAM) up to m5.24xlarge (96 vCPUs/384 GiB RAM).
Larger sizes increase CPU count (measured in vCPUs), memory size (in GiB), storage capacity/type, and network bandwidth.
What Is a vCPU?
A vCPU stands for “virtual CPU.” In AWS:
On Intel/AMD platforms: 1 vCPU = 1 hyperthread of a physical core
On ARM-based Graviton: 1 vCPU = 1 core
This means two vCPUs may share one physical core's resources if hyperthreading is enabled.
Memory Units: GiB vs GB
AWS uses gibibytes (GiB) instead of gigabytes (GB) when listing memory:
1 GiB = 1024^3 bytes
1 GB = 1000^3 bytes
Always check which unit you're reading!
Bare Metal Instances
Some sizes end with “metal” (e.g., m5.metal). These provide direct access to underlying hardware—no virtualization layer—which benefits certain high-performance workloads.
How to Choose the Right EC2 Instance Size?
Selecting an EC2 size requires balancing performance needs against cost constraints. Let's break down this process step by step—from basics through advanced considerations.
Step 1: Define EC2 Workload Requirements for Optimal Instance Sizing
Start by mapping out what your application actually needs:
1. Estimate peak CPU usage—how many processes run at once?
2. Calculate required memory—does your app cache lots of data?
3. Consider storage demands—is fast SSD needed? Or just bulk HDD space?
4. Think about network traffic—will you serve thousands of users at once?
For simple web apps or test environments? General purpose types like t3.medium often suffice. For analytics? Memory optimized r6g.xlarge might be better suited.
Step 2: Compare EC2 Storage Types and Performance Trade-offs
EC2 supports two main storage models:
Most instances use Amazon EBS volumes—persistent block storage attached over network
Choose between gp3/gp2 SSDs for general use; io1/io2 SSDs if you need high IOPS; st1/sc1 HDDs for throughput-heavy jobs
EBS persists even if you stop/reboot an instance
Some types offer local “instance store”—fast NVMe SSDs physically attached to host server
Data disappears when you stop/terminate/rescale these instances!
Storage optimized families like I3 rely on this model
Choose based on whether persistence or speed matters most.
Step 3: Evaluate EC2 Network Bandwidth Based on Traffic Needs
Network bandwidth scales with size within each family:
For example: m5.large provides up to 10 Gbps; m5.24xlarge delivers up to 25 Gbps.
High-throughput applications benefit from larger sizes—or enhanced networking features like Elastic Network Adapter (ENA).
Step 4: Build a Scalable Architecture Using EC2 Instances
Ask yourself:
Can my app scale horizontally? That is—can I add more small instances rather than making one huge?
Horizontal scaling improves resilience but may require load balancers
Vertical scaling means resizing existing instances upward—but there are limits per region/account
Consider both approaches depending on your architecture!
Step 5: Calculate EC2 Instance Costs and Optimize Budget
Larger sizes cost more per hour—but running many small ones can also add up! Use the AWS Pricing Calculator before launching production systems.
Don't forget about additional charges—for EBS volumes/network transfer/data backups/etc.—when budgeting total spend.
Step 6: Monitor EC2 Performance and Fine-Tune Instance Size
Launch candidate instances; run benchmarks under real-world loads; monitor resource utilization using Amazon CloudWatch metrics such as:
CPUUtilizationMemoryUtilization(requires custom agent)DiskReadOps,DiskWriteOpsNetworkIn,NetworkOut
Set alarms if usage exceeds safe thresholds—for example above ~70% sustained CPU utilization during business hours signals possible undersizing!
If needed? Stop your instance via AWS Console > Actions > Instance State > Stop; then select Actions > Instance Settings > Change Instance Type; pick new size; restart it again via Start button.
Comparing Popular EC2 Instance Families & Sizes
Understanding differences between major instance families helps match them precisely with workloads—from entry-level projects all the way up through enterprise-scale deployments.
General Purpose Instances
These strike a balance between compute/memory/networking:
| Family | Example Size | vCPUs | Memory | Network | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M5 | m5.large | 2 | 8 GiB | Up to10Gbps | General-purpose web/app servers |
| m5.xlarge | 4 | 16 GiB | Up to10Gbps | Small DBs | Small to medium-sized databases |
| m5.12xlarge | 48 | 192 GiB | 10Gbps | Enterprise apps | High-performance enterprise applications |
| m5.metal | 96*† | 384 GiB† | 25Gbps† | Bare metal | Bare metal workloads needing full hardware access |
\*vCPU count varies by generation
†Check latest specs in AWS Console
Newer generations improve efficiency:
> M6i/M7g offer lower costs per workload compared with older M4/M5 series due to improved CPUs—including ARM-based Graviton chips in M7g!
T-series burstable types like t4g.micro are ideal for dev/test environments—they accrue “credits” during idle time that allow brief bursts of higher performance when needed.
Compute Optimized Instances
Best choice where raw processing power matters most:
| Family | Example Size | vCPUs | Memory | Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6i | c6i.large | 2 | 4 GiB | Up To12.5Gbps |
| C6g | c6g.xlarge | 4 | 8 GiB | Up To12Gbps |
Use cases include scientific modeling/batch jobs/high-frequency trading.
Memory Optimized Instances
For applications needing massive RAM allocations:
| Family | Example Size | vCPUs | Memory |
|---|---|---|---|
| R6i | r6i.large | 2 | 16 GiB |
| R7g | r7g.xlarge | 4 | 32 GiB |
SAP HANA/big data analytics/in-memory caching thrive here.
Vinchin Backup Solutions for Modern Virtual Infrastructures
Once you've selected the right AWS EC2 instance size, ensuring the protection and recoverability of your cloud workloads is the next priority.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers enterprise-grade backup and recovery for virtual environments—including AWS EC2—supporting over 15 platforms such as VMware, Hyper-V, Proxmox VE, oVirt/RHV, XCP-ng, and more. With features like forever-incremental backup, built-in deduplication, file-level backup, and seamless V2V migration across cloud and on-premises platforms, Vinchin helps enterprises protect critical systems efficiently via a simple, centralized web console.
To back up an AWS EC2 using Vinchin's web interface is straightforward:
1.Just select the AWS EC2 on the host
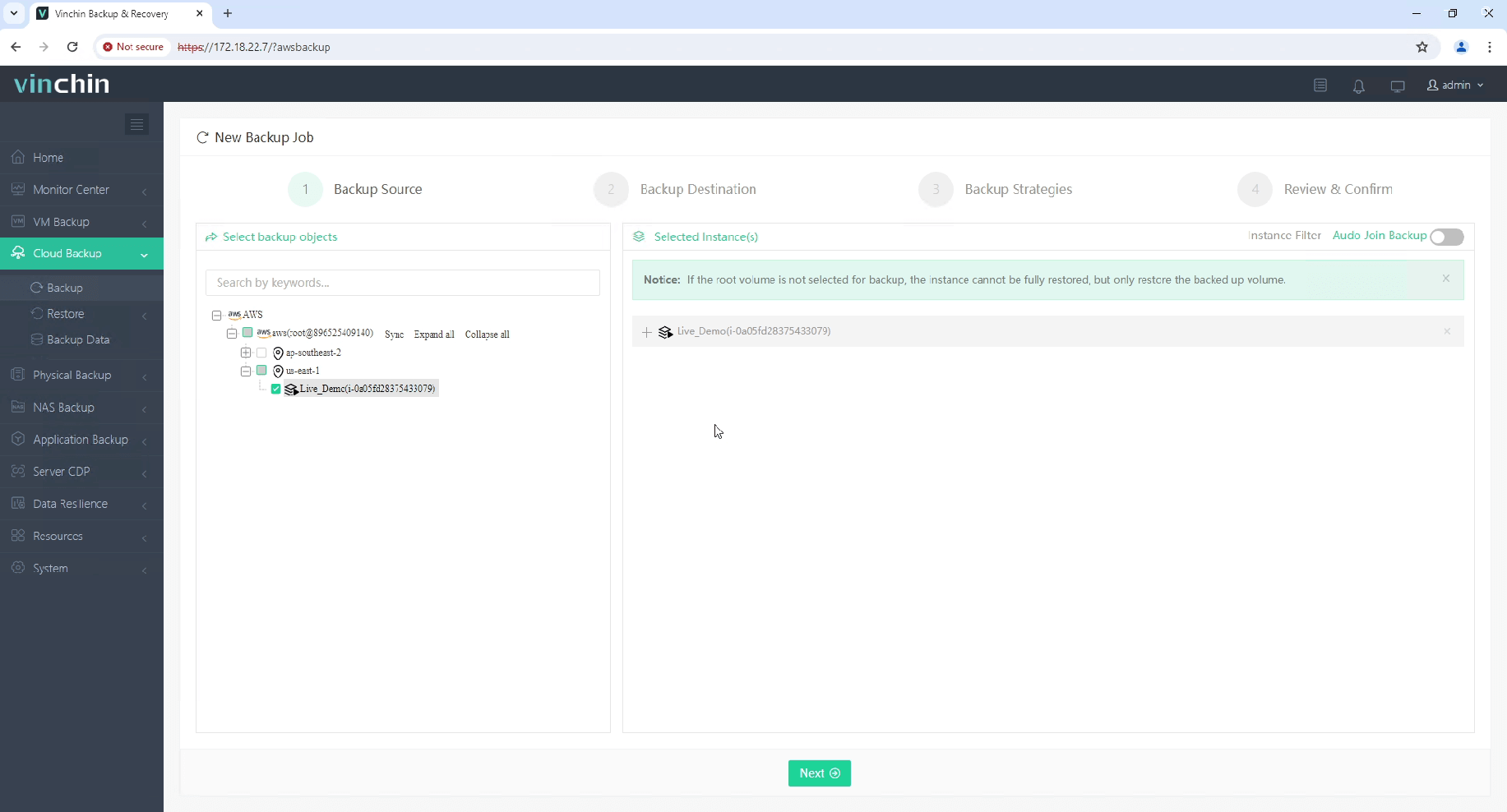
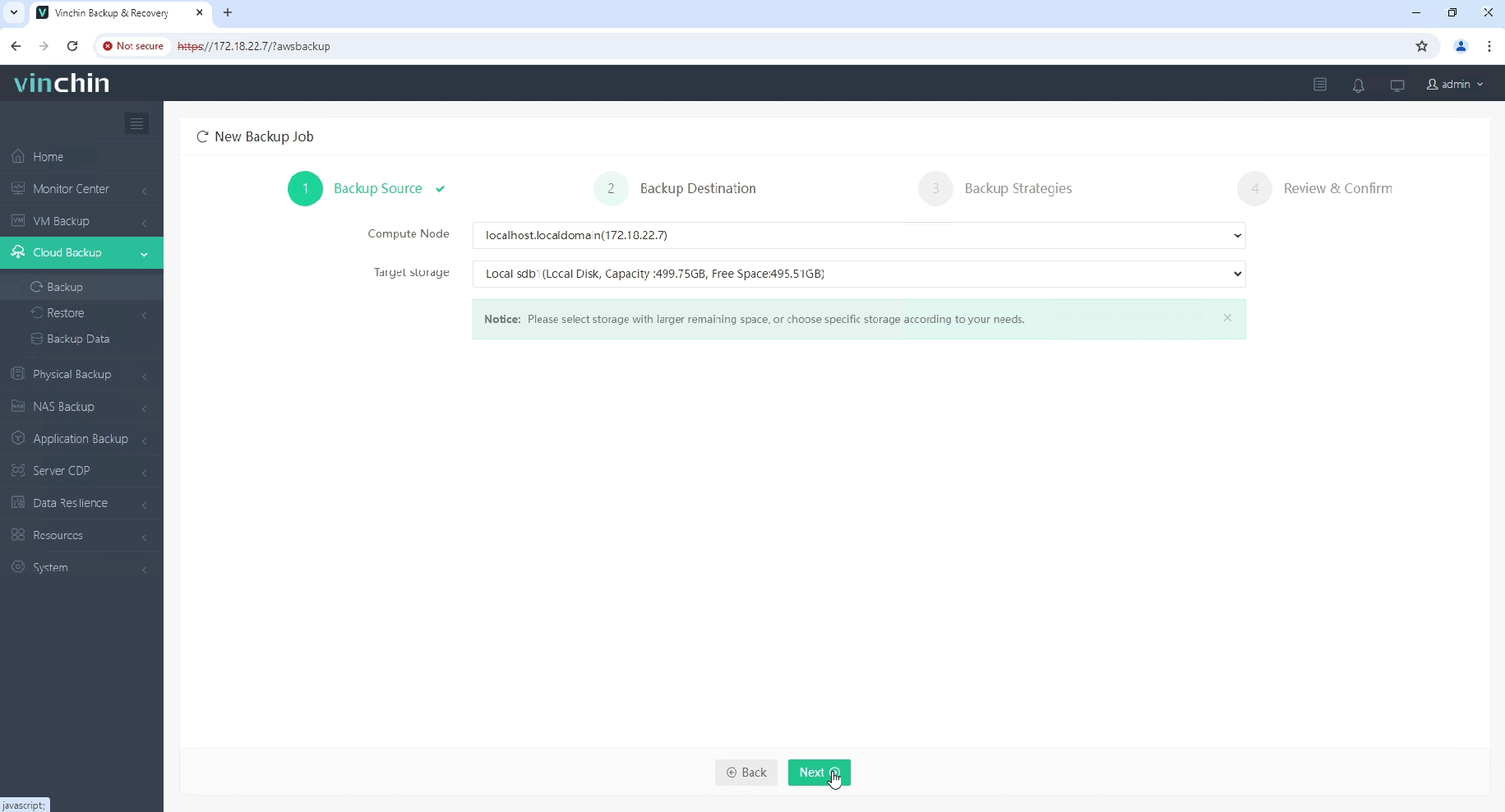
2.Then select backup destination
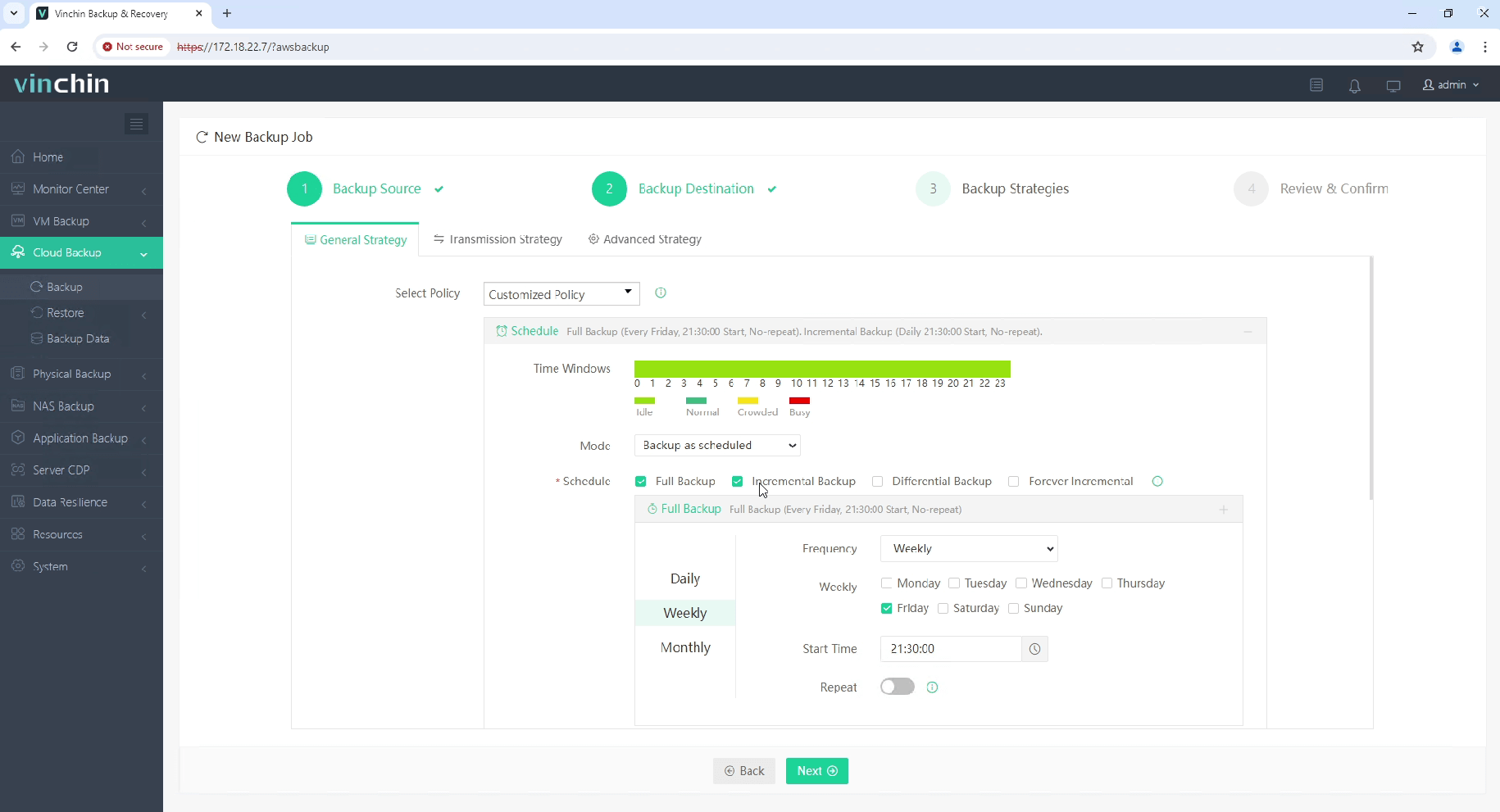
3.Select strategies(including incremental backups)
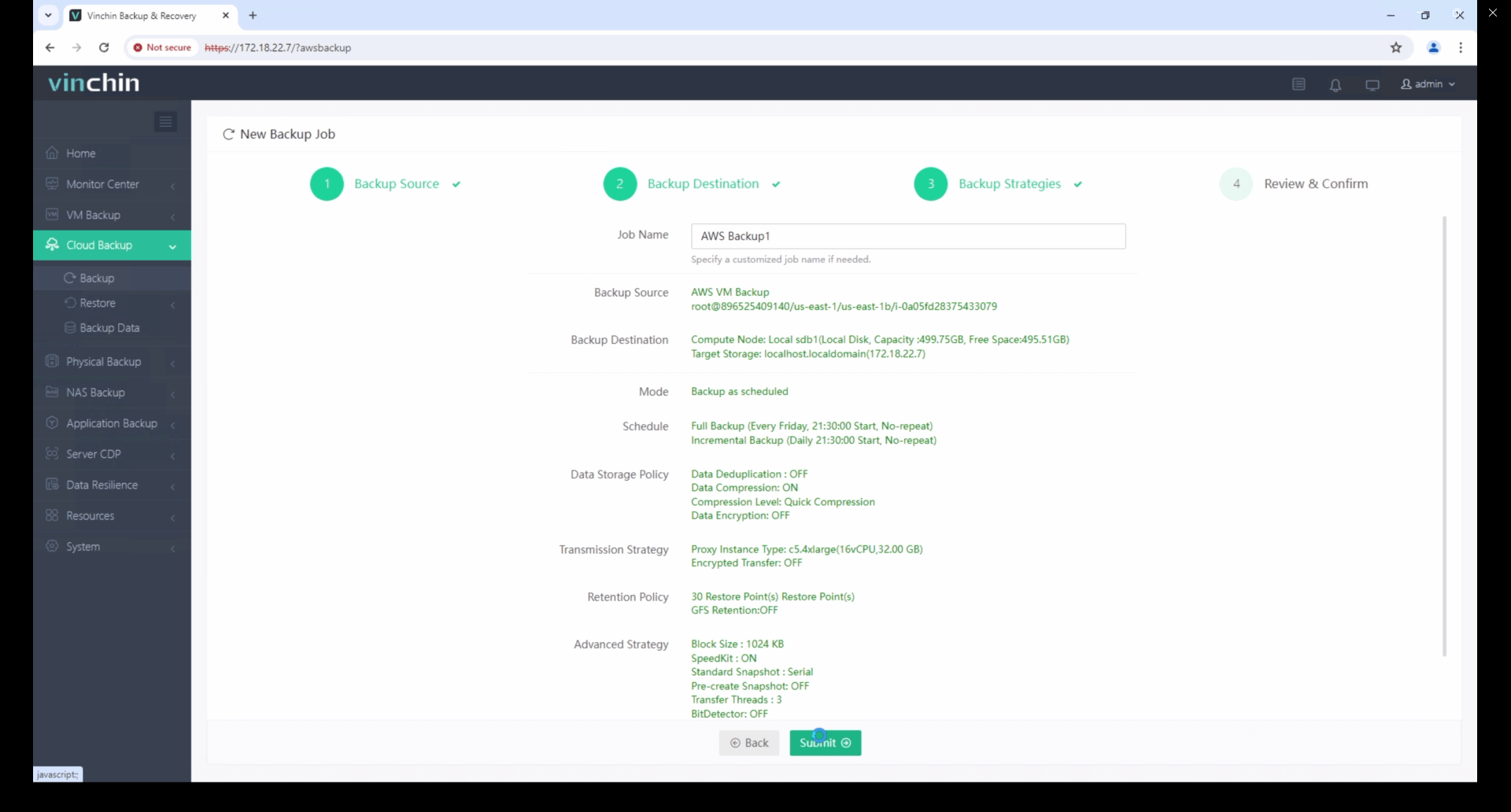
4.Finally submit the job
Vinchin offers a 60-day free trial, allowing you to explore its full feature set in real-world environments. If you're interested in simplifying backup and recovery across AWS EC2 and other platforms, feel free to contact us for more information or personalized assistance.
AWS EC2 Sizes FAQs
Q1: Can I resize an EC2 instance without downtime?
A1: No. You need to stop the instance first, then go to Actions > Instance Settings > Change Instance Type, and restart it afterward.
Q2: How does instance size impact EBS performance?
A2: Larger instance sizes offer higher EBS bandwidth and IOPS. Refer to the AWS documentation for exact limits by instance family.
Q3: What happens if I overuse a burstable (T series) instance?
A3: If you exceed your CPU credits, performance will be throttled until you accumulate or purchase more credits.
Conclusion
Choosing the right AWS EC2 instance ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency for your workloads. From sizing strategies to instance families, this guide covered it all. For added protection, Vinchin offers streamlined, enterprise-grade backup for EC2 and beyond—making VM data security simple, scalable, and reliable across hybrid environments.
Share on:







